Administration of a hospital’s MRD is not exactly glamorous; however, it is an important aspect of health administration. In the absence of proper management of the MRD, gathering information about a patient, compliance, and maintaining confidentiality would pose an actual challenge. A well-organized MRD does not simply keep things tidy; it directly impacts patient care, hospital efficiency, and regulatory compliance.
With this guide, discover why MRD management is more important now than ever and how hospitals can better optimize this mission-critical function. You’ll learn everything the hospital administrator, healthcare IT professional, and compliance officer need to know, including the role of MRD and leveraging technology to meet strict regulations.
MRD Management: What It MRD Full In Hospitals, Why It Matters

First, get an understanding of the MRD full form in hospitals and its context before discussing the details about MRD management. The MRD forms the hub of the hospital information system. This is the place where creation, storage, and maintenance of patient records take place. The record contains the complete medical history of a patient, which forms the basis for treatment decisions and ensures continuity of care.
Why MRD Management is Important
There are many reasons as to why this department has to be managed efficiently. Accurate and timely medical records assist health professionals in decision-making, minimize errors, and improve patient outcomes. A well-managed MRD means smooth flow in the operation for the administrators and compliance with the regulations in healthcare. Compliance officers depend on these systems to show legality in retention policies and laws on confidentiality.
Poor management of MRD places hospitals at risk for delays in access to patient information, treatment errors, and fines for non-compliance. It is not only a question of maintaining orderly records but an ongoing flow of information that will support every facet of hospital operations.
Key Benefits of Effective MRD Management
Efficient management of MRD is not only a back-office operation but is a huge success driver for a hospital. Here are some major benefits that explain its importance:
Speedier Access to Information
A well-organized MRD enables health professionals to locate patient records in less time. This, in turn, leads to quicker diagnosis, timely treatment, and better patient outcomes. For the staff at the hospital, reduced retrieval times mean smooth workflows and a decrease in administrative delays.
Improved Data Security and Privacy
Medical records contain sensitive information, and hence security is a key issue. Efficient management of MRD ensures that data will be stored securely and accessible only to authorized persons, reducing the possibilities of breaches, hence earning trust among patients.
Improved Compliance with Regulations
A set of laws governs the management, storage, and disposal of medical records in hospitals. The effectiveness of an MRD ensures adherence to regulations involving but not limited to HIPAA and GDPR; it protects the hospital from fines and reputational damage.
Reduced Administrative Burden
When MRD processes are optimized, less time will be spent on searching or updating records by the staff. Automated systems cut down on manual labour, freeing up resources for other critical tasks.
Improved Continuity of Care
Accessible and proper records facilitate smooth transitions among healthcare professionals. Whether the patient is being referred to a specialist or moving between departments, MRD management supports continuity of care with a complete picture of the patient’s medical history.
Cost Savings
Efficient MRD operations minimize storage costs, with the potential of digital systems reducing this even further. Besides, automated workflows cut down on errors and, therefore, save money that would have been spent by the hospital in corrections or reworking.
Informed Clinical Decisions
Complete and timely patient information allows for the best clinical decisions. Physicians will be able to look for trends, identify risk factors, and tailor treatments for better patient satisfaction and overall outcomes.
These advantages constitute a strong case for managing the MRD in hospitals. Now, we explore common challenges faced by hospitals and ways to overcome them.
MRD Management Challenges
While the benefits of good MRD management are seemingly obvious, numerous barriers often stand between most hospitals and an optimized system. These can cause bottlenecks, affect patient care, and may even expose hospitals to certain regulatory penalties.
Reliance on outdated systems
The majority of hospitals either still use paper-based systems or employ outdated software incapable of keeping pace with the demands today. These are error-prone, costly to maintain, and time-consuming to update.
Data Security Risks
Medical records are considered very sensitive information, and that places them in the crosshairs of cyberattacks. The risk, should there not be adequate security to prevent this, includes data breaches, legal ramifications, and loss of reputation for hospitals.
High Storage Costs
Physical storage for paper records occupies a large space and requires heavy maintenance. As the number of patients increases, the storage costs rise proportionally; it is an unjustified solution even for many hospitals.
Interoperability is Lacking
Systems that are disparate-whether within a hospital or between healthcare providers-create barriers to sharing patient records, delays in care, and possible errors due to a lack of integration.
Compliance Complexities
Medical records management is one of the most heavily regulated areas in healthcare, with constantly changing regulations. Many hospitals are unable to keep pace with the demands for compliance and risk receiving heavy fines or legal consequences.
Poor Training
Inadequate training of staff in MRD processes or software can lead to their introduction of errors. Training gaps also make the pace of adoption of new technologies much slower, hence reducing their effectiveness.
Time-Consuming Record Retrieval
Inefficient systems delay patient record retrieval, a factor that slows down decision-making processes and frustrates patients, thus putting pressure on the staff needlessly.
Role of Technology in MRD Management
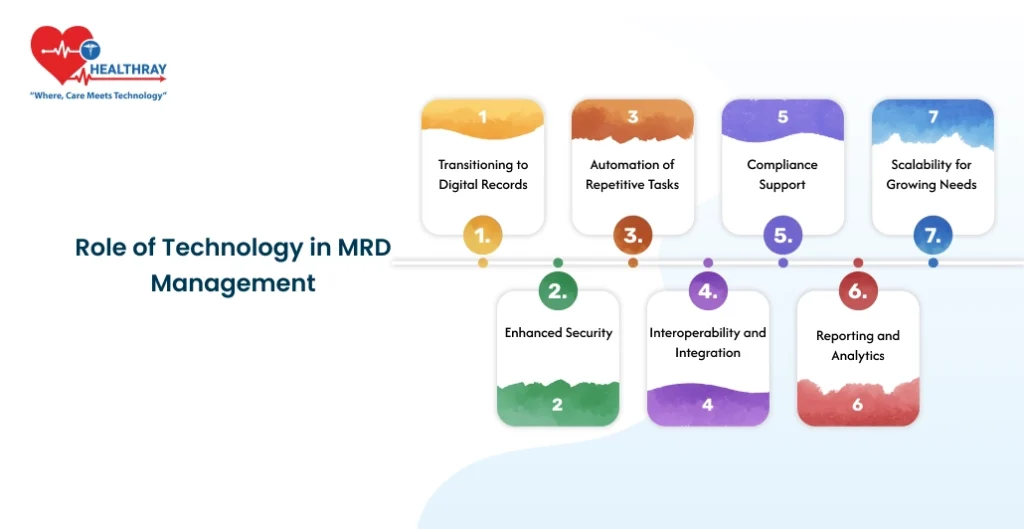
Technology has transformed the way hospitals manage their medical records, turning what was once a generation of drudgery into one of speed, security, and efficiency. In harnessing these digital tools, day-to-day operations are only a few of the pressing problems faced by hospitals.
Moving to Digital Recordkeeping
The shift from paper-based systems to EMR removes all the inefficiencies related to manual record-keeping. Digital records reduce storage space, enhance the speed of retrieval, and minimize errors related to illegible handwriting or misplaced files.
Improved Security
Advanced security features are available on modern MRD systems, such as encryption and multi-factor authentication. Safeguards such as these protect sensitive patient information from unauthorized access, hence considerably reducing the risk of data breaches.
Automation of Repetitive Tasks
Consequently, HMS saves time by automating workflows, hence minimizing the incidence of human errors. The indexing, entry, and retrieval of records are all done seamlessly to free up the staff for more critical responsibilities.
Interoperability and Integration
Technology allows smooth sharing of data between departments, let alone various healthcare providers, in a hospital setting. Interoperability ensures that patient records are available whenever these are needed to support better coordination and continuity of care.
Compliance Support
The MRD software is designed to adhere to all regulatory standards such as HIPAA or GDPR. Inbuilt compliance checks, automated audit trails, and timely alerts will assist the hospitals in moving ahead regarding evolving regulations.
Reporting and Analytics
Advanced systems offer robust analytics to empower administrators with the ability to monitor MRD performance and trends in their patient populations. Customizable reports expose opportunities for improvement and help make informed, data-driven decisions.
Scalability for Growing Needs
Digital systems can expand to meet growing patient volumes and, especially important, cloud-based solutions that allow hospitals to flexibly ramp up their MRD capacities without major investments in infrastructure.
Best Practices in MRD Management
AI-enabled MRD management is far more than the deployment of technology. It is a strategic initiative that integrates systems, processes, and people to ensure records are accurate, accessible, and secure. Here’s a look at some best practices that a hospital can adopt to optimize the operations of MRDs:
Standardizing procedures
Develop clear, standardized methods of creating, maintaining, and retrieving records. Uniformity ensures that all staff in every department use the same methods; hence, it cuts down on errors and boosts efficiency.
Train the staff regularly.
Invest in regular training sessions for all employees that are involved in MRD operations. They should be aware of compliance requirements of the work, use the MRD software, and be adequately equipped to handle updates or changes.
Digitize records
If your hospital still uses paper records, then there is a great need for digitizing such information. Digitization saves storage space, makes record retrieval easy, and improves security.
Perform Routine Audits
Auditing MRD processes on a regular basis helps them meet regulatory requirements and points the way for improvement. Use the audits to find inefficiencies, address security gaps, and further refine workflows.
Implement Access Controls
Ensure role-based access to patient medical records. Strong access controls reduce the chances of unauthorized access and protect patient confidentiality.
Use cloud-based solutions
Look into cloud-based MRD systems to store data offsite, taking into consideration scalability and security. Cloud-based solutions allow access remotely, with automated backups and options for disaster recovery.
Monitor Data Quality
Ensure accuracy of the information contained in the records. Keep regular updates of patient information to ensure that all the records are accurate and without error.
Respect Patient Privacy
Comply with legislation such as HIPAA by implementing measures that ensure data protection. Training of staff in regard to privacy practices, as well as implementation of technology solutions that meet industry security standards.
Plan for Emergencies
Design a disaster recovery plan for medical records, ensuring the restoration of data in as short a time as possible in the event of system failure, natural disasters, or cyberattacks.
Engage Leadership
Get the buy-in of hospital leadership for the prioritization of MRD improvements; this buys into leveraging adequate resources, funding, and staff commitment downwards.
Applying these best practices allows hospitals to establish an MRD system which is supportive of efficiency in operations, regulatory compliance, and quality patient care.
Regulatory Requirements for MRD

A most important constituent in MRD management is compliance with the rules and regulations associated with health care. In hospitals, there exist tight rules regarding access, storage, and disposal of the medical records; noncompliance invites legal consequences, monetary fines, and loss of reputation.
Key Regulations Affecting MRD
- HIPAA: The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act states that all PHI must be kept safe. In all hospitals, the records are to be kept in a secured area, with controlled access, and disposed of properly.
- General Data Protection Regulation: The GDPR in Europe regulates the collection and processing of personal data, such as medical records in hospitals. The central elements are consent and transparency.
- Local Laws and Guidelines: Retention time and standards for medical records differ among different countries. The hospitals should keep themselves updated about the regional requirements.
Record Retention Policies
Set clear policies regarding how long to maintain records. For example, in many jurisdictions, it is required that the records of adult patients be retained for a minimum of 5-10 years beyond the date of the last treatment; pediatric records generally require longer retention periods.
Regularly check and revise policies to be in line with new regulations.
Data Privacy and Security
Ensure robust data encryption to protect patient information both in storage and transit.
Employ role-based access so that only authorized personnel can access sensitive data.
Perform security audits periodically to identify and address vulnerabilities.
Disposition of Records
Specify safe methods of record disposal when the retention period expires. Among physical records, shredding is the most common; among digital records, permanent deletion using specialized tools should be performed.
Audit Readiness
Document comprehensive records regarding MRD policies and procedures.
Audit trails provide a way of tracking who accesses, modifies, or deletes records.
Perform periodic internal audits to meet compliance requirements of regulatory standards.
Staff Training in Compliance
Train employees on the importance of data privacy, security practices, and legal requirements.
Offer refresher courses to put them abreast of changes in regulations.
Measuring the Success of MRD Management
To ensure that MRD management strategies are effective, hospitals should closely monitor their progress by using measurable metrics. Regular evaluation will not only identify areas needing improvement but also ensure compliance with operational goals and standards.
Key Metrics to Track
- Time to Retrieve Record: This measures the time taken before access to a patient record is obtained. Faster retrieval indicates better systems and smoothly flowing workflows.
- Medical Record Error Rates: Monitor discrepancies or missing information within medical records. A smaller percentage indicates higher quality data and staff accuracy.
- Compliance Audit Results: Assess the degree to which the hospital complies with regulatory requirements. In other words, positive audit results reflect good management practices of MRDs.
- Patient Record Availability: Determine if there are available records within or across departments and/or healthcare providers, as this indicates interoperability.
- Storage costs: The cost of physical and/or digital record storage. A decrease demonstrates that cost-saving measures, such as digitization of records, have been successful.
- System Downtime: Frequency and duration of MRD system downtime. Downtime should be at a minimum to indicate good technology and disaster recovery plans.
Performance Monitoring Tools
- Analytics Dashboards: Most HMS solutions are now offering inbuilt analytics for monitoring key performance indicators and report generation.
- Surveys and Feedback: Obtain feedback from staff and patients on how easily records are accessed and the general efficiency of the MRD process.
- Periodic Audits: Internal audits shall be conducted to assess compliance, data quality, and adherence to standardized procedures.
Setting Benchmarks
- For each metric, clearly define its benchmarks using either industry standards or organizational goals.
- For instance, try to fetch records in under one minute, or achieve a compliance score of 95% or higher in internal audits.
Improvement Driven by Insights
- Look for bottlenecks, like slow retrieval times or frequent errors, using metrics analysis.
- Implement focused interventions, such as additional training or enhanced technology, to address weaknesses.
- Regularly review the benchmark and adjust according to changing hospital needs and updates in regulations.
Conclusion
Effective MRD management is much more than a back-office function; rather, a fundamental driving force in efficiency in hospitals, patient safety, and regulatory compliance. Prioritizing record-keeping accuracy, embracing technology, and following best practices are ways a hospital can avoid such challenges as inefficiencies, data security risks, and compliance gaps.
Real benefits flow from investment in MRD improvement, from quicker record retrieval and cost savings to improved continuity of care and informed clinical decisions. Hospital administrators, healthcare IT professionals, and compliance officers each have key roles to play in driving these improvements and in assuring that the MRD supports the greater mission of the hospital.
Now is the time to assess the present MRD practices within your hospital and avail the opportunities for optimization. Be it upgrading to a digital system, training staff, or putting in place measures for strict compliance-whatever you do towards efficient management of MRDs strengthens the very foundation on which your hospital runs.