Summary
Interoperable EHRs allow investigators to send patient data from one hospital to another and are changing the delivery of healthcare. The improved EHR software increases access in real-time and allows quicker decision-making with decreased error rates, leading to increased patient outcomes and staff productivity.
For hospitals and clinics, EHRs help coordinate patient care, share information securely and improve clinical workflows. Interoperability will improve efficiency, reduce unnecessary diagnostics, and improve patient safety. Part of this preparation is to prepare the industry for the new smart and connected future of our health care.
Introduction
Hospitals today have endless amounts of patient data, but most systems still don’t “talk” to each other. The results? Confusion, retesting, and wastage of time.
But imagine every doctor, every nurse, every lab having that patient information instantly – with no delays and no screwing it up. Sounds magical, right? But it’s already happening with interoperable EHR.
This form of smart technology unifies each department through robust EHR software, which connects patient data into one system. It can save time, reduce mistakes and improve teamwork in hospitals. The patient experience is also more seamless and safer as patients do not have to repeat their medical history. This is one of the great benefits of electronic health records: a quick translation of chaos into clarity.
In this post, we’ll explore what interoperable EHRs really are, why they are so important to modern hospitals, how they work and how they are transforming the patient experience.
What is an Interoperable EHR?
An Electronic Health Record (EHR) is a digitized version of a patient’s health history. It’s an online health record that centralizes everything from diagnoses to test results, prescriptions and treatment notes in one secure location.
But an interoperable EHR takes it a step forward. It not only stores, but also transmits data to other systems, hospitals and clinics in real time. It connects every nook and cranny of health care, from labs to pharmacies to specialists to emergency rooms, exchanging data with seamlessness.
Standard EHRs are in use and effective in only one system, whereas interoperable EHRs communicate and are effective across multiple systems. So, if a patient walks into Hospital A, for example, doctors there can send their records instantly, without emails, phone calls or paperwork, to Hospital B. The instant exchange of those kinds of health records improves accuracy, accelerates care and saves lives.
Levels of EHR Interoperability
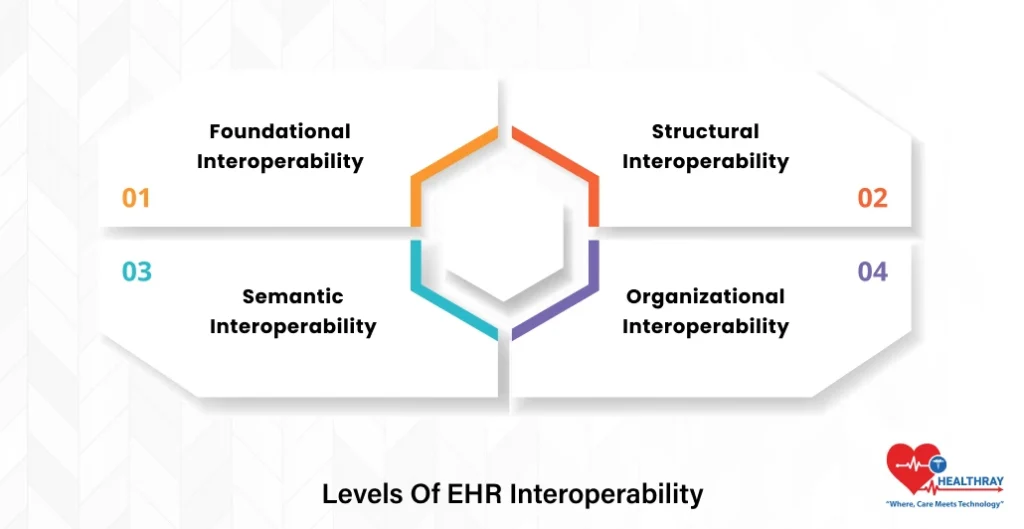
An interoperable EHR functions on multiple levels.
Foundational Interoperability
This is the lowest level of interoperable EHR. It allows two systems to safely exchange digital health records, even if they do not fully share understandings of the data. It’s like sending a file from one hospital to another: one system transmits, another one receives.
Structural Interoperability
At this point, the data exchange is more formalised. It is normalized so that it can all be understood and rendered appropriately by any EHR software. This means that tiny bits of information, like patients’ names, test results and medications, are everywhere they are supposed to be.
Semantic Interoperability
Here, systems not only exchange but also understand the semantics of the exchanged data. For example, BP is always blood pressure, no matter which hospital you are in. This common understanding increases accuracy, decreases time to diagnosis, and increases care for patients.
Organizational Interoperability
This highest category ensures that hospitals, clinics and all other care providers use the same data exchange policies, workflows and governance rules. When organizations adopt these standards, digital health records can flow smoothly and securely through the healthcare network.
Key Features of an Interoperable EHR System
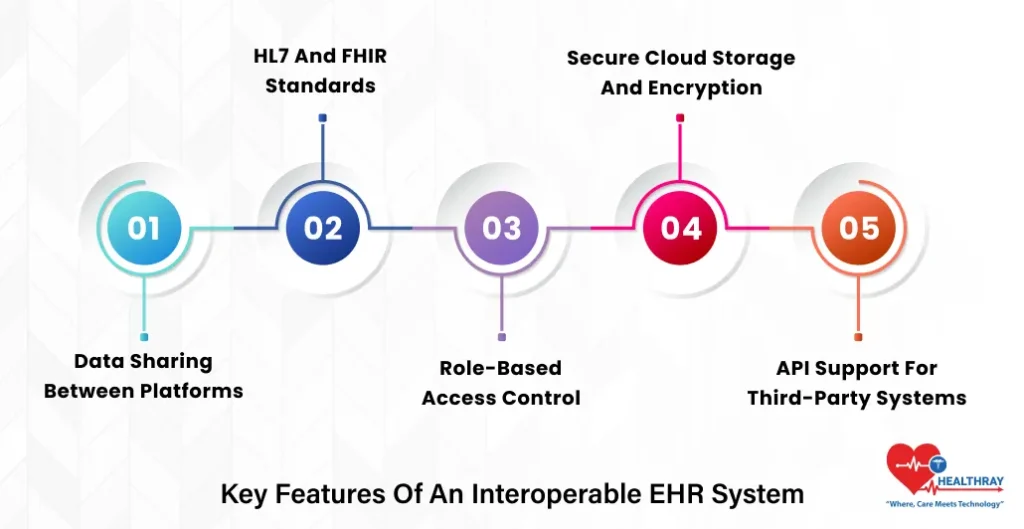
To really enable connected care, the next generation of EHR software must include certain must-have features that ensure optimal data flow and security, as well as seamless collaboration. Let’s take them one at a time.
Data Sharing Between Platforms
Integral to successful EHR implementation is seamless sharing of data. It enables hospitals, clinics, and labs to share patient information instantly, regardless of the systems they use.
With doctors able to access a patient’s complete medical records at any point over the network, decisions can be faster and safer. And it reduces redundant tests and duplicate records, both of which cost time and money. This type of real-time, cross-platform communication is one of the major benefits of electronic health records, enhancing quality of care and the patient experience.
HL7 and FHIR Standards
In order for communications between systems to occur, they need to be able to “speak the same language”. Universal standards, like HL7 (Health Level Seven) and FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources), make this possible. They allow EHR software data to flow freely from one system to another without compatibility issues.
By adhering to these standards during EHR implementation, healthcare institutions can ensure their systems do not conflict with one another and mitigate the risk of data loss or corruption. So, HL7 and FHIR serve as universal bridges among systems, ensuring correct and reliable data exchange.
Role-Based Access Control
Healthcare security and privacy are of utmost importance, particularly in the context of sensitive data and EHR software. Users with appropriate permissions can see or edit only the patients they are authorised to access. Doctors, nurses and administrators each have access only to the data they require.
This protects patients’ privacy while allowing transparency within the team. In addition, the appropriate use of access management strengthens trust among patients, which is one of the essential benefits of electronic health records.
Step towards digital era with our healthcare solution
Revamp your hospital facilities and embrace change for better healthcare management. Ease in managing and organizing large medical datasets leads to effective analysis. Seize the opportunity now!
Secure Cloud Storage and Encryption
Modern EHRs also use cloud technology for scalability and flexibility. Patient data is securely stored offsite in the cloud and is immediately accessible on any authorised device.
Data in transit and at rest is also encrypted through sophisticated techniques, which minimises exposure to cyber-attacks. And with cloud-like systems, records are never lost as backups and disaster recovery are built in and automatic. This security feature only enhances the benefits of electronic health records by ensuring patient information is available without compromise.
API Support for Third-Party Systems
A solid EHR needs to be able to interface easily with other healthcare products—such as billing systems, pharmacy applications, or diagnostic platforms. This is where API (Application Programming Interface) support is important.
APIs are like digital connectors that allow third parties to connect to the core EHR software. This flexibility enhances EHR implementation by allowing hospitals to customise their systems instead of having to rebuild the system from scratch. The result? An integrated platform designed for the future of healthcare that will evolve with it and seamlessly interface with the next big things.
Why Interoperable EHR Matters for Hospitals?
Here’s why EHR For Hospitals & Clinics is a game-changer.
Faster Access to Patient Data
With interoperable EHR, doctors and nurses can instantly see complete patient information, lab results, medications, allergies and history from any device and location. This means no lag caused by paper records or legacy systems.
When done properly, with a strong EHR implementation plan, this instantaneous flow of information will ensure that doctors have the right information at the right time. In hospitals and clinics, faster EHR access means quicker treatments and happier, healthier patients.
Better Decision-Making
Interoperable EHRs provide healthcare teams with a complete picture of each patient’s medical journey. Rather than having access only to incomplete information, physicians can view complete treatment records from other clinics or specialists.
This holistic view enables more intelligent, better-informed decisions. Having lab results, imaging results, and clinical notes all incorporated into one EHR software allows teams to identify patterns earlier and customise treatment plans. This data-driven decision, which reduces risk and improves clinical outcomes, is one of the largest benefits of electronic health records.
Less Test Duplication
Duplicate tests waste time, money and patient energy. With a connected EHR for hospitals and clinics, every provider can see which tests were tried, when, and where. That means no duplicate testing and immediate communication of results across systems.
EHRs are designed to enable data to flow easily between departments and facilities. This leads to more efficient resource use and a better patient experience. This kind of efficiency is yet another main reason why hospitals are migrating to interoperable EHR systems.
Improved Patient Safety
Patient safety increases significantly when information is accurate and up to date and shared by all healthcare providers. Electronic health records, or EHRs, used in hospitals and clinics enable physicians to see in an instant whether a patient has allergies, previous reactions or interactions with any new medication they prescribe.
This real-time insight helps avoid dangerous mistakes and makes patients more confident in their care. Because each edit in the EHR software is recorded and time-stamped, this facilitates accountability and transparency. These safeguards show the great benefits of electronic health records in terms of decreasing human error and enhancing the quality of care.
Better Coordination
Teams are essential in modern hospitals, and smooth coordination begins with shared information. In the case of EHR for hospitals and clinics, nurses, doctors, and technicians can access any patient’s file at the same time. This shared visibility decreases miscommunication, accelerates handovers and aligns all parties on the same treatment goals.
With an appropriate EHR implementation to support it, this process appears seamless. The system is automated, alerts the team in real time, and retains all of the records of what is done. Ultimately, interoperable EHRs make teamwork not manual coordination, but an intelligent, data-driven process with patients still at the centre of care.
How Hospitals Can Achieve EHR Interoperability?
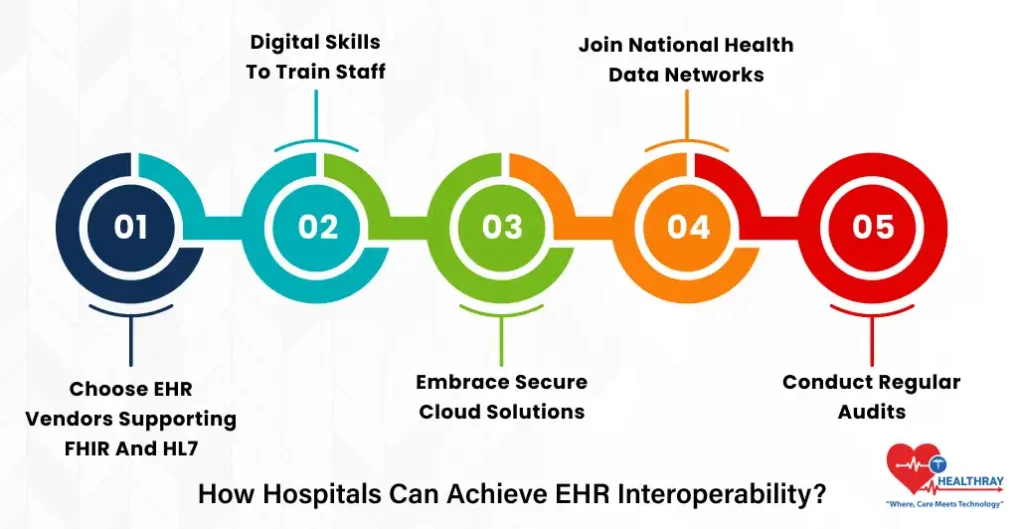
If we follow this roadmap, EHR for hospitals and clinics will lead to transformed patient care and efficiency and will permit data to flow across departments.
Choose EHR Vendors Supporting FHIR and HL7
First and foremost, choose EHR software built on universal standards such as FHIR and HL7. These standards enable interoperability between systems and data exchange, where input from one system is processed in another. Selecting compliant software provides hospitals with a foundation for connected care across facilities.
Digital Skills to Train Staff
Good EHR software will also fail without good staff to operate it. Nurses, doctors and administrative staff also have to learn how to access, read and update these digital health records. Regular training sessions help increase acceptance and minimise errors in the day-to-day use of EHR for hospitals and clinics.
Embrace Secure Cloud Solutions
Cloud computing enables seamless and secure interoperability of patient data across departments and locations. They also provide scalability, encryption, and disaster recovery, making certain that records are accessible and protected. Cloud is a critical part of the eventual successful interoperability of EHR for hospitals and clinics.
Join National Health Data Networks
Joining larger health data networks enables hospitals to share patient information outside their own walls. Integration enables seamless information flow from hospitals to labs to clinics, improving patient outcomes and coordination.
Conduct Regular Audits
Finally, conduct regular audits to check data quality, security, and compliance. The audits are used to find weaknesses in a workflow or a system. This helps the hospital improve its EHR software instances and maintain interoperable EHRs, fulfilling its promise.
Conclusion
Interoperable EHRs represent the backbone of contemporary healthcare, where the amalgamation and integration of data can create a powerful system. With intelligent EHR software, hospitals can eliminate waste, increase accuracy and improve patient outcomes.
In the case of EHRs for hospitals and clinics, this means quicker access to vital information, better decision-making, and safer care for every patient. And each step toward interoperability reinforces teamwork and facilitates real-time interaction between departments and facilities. Digital health records that are harmonised and interoperable will be the future of healthcare. Remember, when data moves, healthcare improves, smarter, faster, and more patient-focused than ever before.




