The AI-powered hospital management systems are rewriting the data management rules for the healthcare organizations. Powered by artificial intelligence, these systems at managing, analyzing, and storing health data offer increased speed and accuracy with efficiency in operations. Healthcare administrators are impressed by the promise of streamlined workflows, whereas tech developers find it an avenue to innovate patient care.
The possibility of handling extraordinary volumes of sensitive health data is the main attraction with these systems while minimizing manual errors. With compliance to regulations and predictive analytical modeling for decision support, these systems are atmosphere-changing for the future of healthcare.
Like any new wave of technology, they come with their own challenges and benefits. This post will discuss how these systems contribute to the success of healthcare organizations and the challenges still in sight. Stay tuned to see and determine whether one is worth the investment.
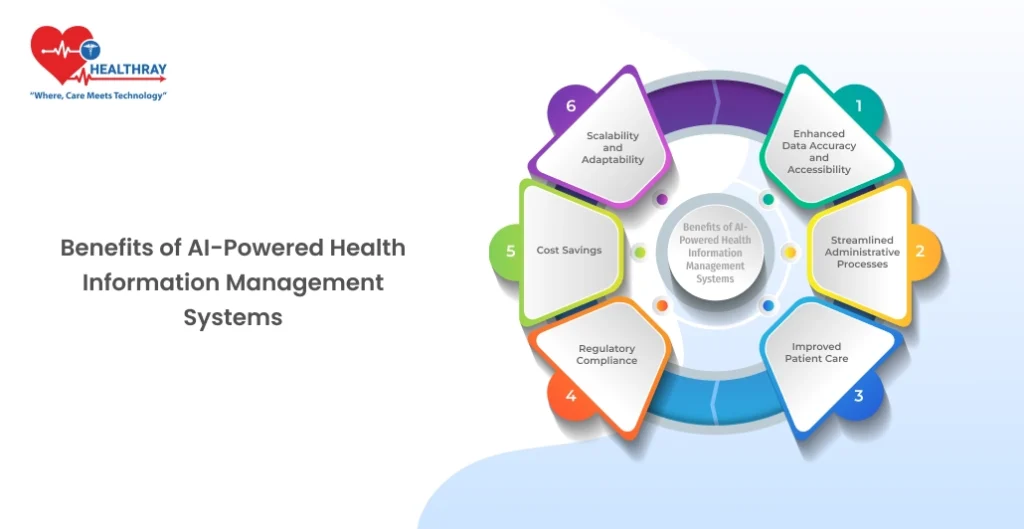
Benefits of AI-Powered Health Information Management Systems
Benefits Of Ai-powered Health Information Management Systems – Healthray
Healthcare organizations are increasingly adopting AI-powered Hospital Information Management Systems because of the tangible improvements these systems afford them in operations and patient care. Here are some great benefits:
Enhanced Data Accuracy and Accessibility
AI systems can analyze large amounts of data with minimal errors. They also centralize patient records such that authorized persons in all departments can access them. This would impair any miscommunication while ensuring that care providers have real-time information at all times.
Smoothened Administrative Processes
In automating administrative work, repetitive activities like billing, appointment scheduling, and processing of claims are removed from the staff’s notice list for more critically engaged chores. This, in turn, enhances overall efficiency and cuts the risk of delays or mistakes in the administrative workflow.
Improved Patient Care
AI helps begin to recognize patterns possibly missed by human analysis in the context of patient data, whereby predictive analytics might warn doctors of a future health risk prior to its escalation so that early intervention may be undertaken, improving patient outcomes.
Regulatory Compliance
To be sure, remaining compliant with a myriad of regulations that constantly keep changing in healthcare presents a serious headache. The AI-powered systems help to monitor data and workflows to ensure compliance with policies such as HIPAA. They also maintain thorough records that are invaluable during audits.
Cost Saving
Their long-term cost cuts will, however, surpass the very high initial investment since they help optimize the way resources are utilized, eliminate waste, and avert costly errors. Automating tasks that would otherwise have cost a lot in human labor is itself a cost-cutting measure.
Scalability and Adaptability
As healthcare organizations grow, the amount of data being handled also grows. AI systems thereby become scalable in their ability to take on an increased workload without compromising on quality and can also adapt to changing technologies – making them future-proof investments.
Artificial Intelligence in Health Information Management Systems: Challenges

In the long run, AI systems promise to bring unassailable benefits to heath organizations, but the adoption road is fraught with challenges that have to be merchandised carefully by healthcare organizations and the tech developers. Here are the most important issues at stake:
Data Privacy and Security Concerns
Healthcare data is highly sensitive whose breach can lead to severe legal and financial consequences. AI systems, although very advanced, cannot be divorced from cyber risks. Organizations must invest in strong security measures to protect unauthorized access to patient record management systems.
High Implementation Costs
Integration of AI systems incurs upfront costs that form considerable barriers especially for the small healthcare providers. The costs are associated with hardware upgrades, licensing software, staff training, and ongoing maintenance.
Complex Integration
The difficulty lies in seamless incorporation of AI system into legacy software and hardware, which frequently proves complex. Moreover, incompatibility has the potential to result in delays and extra expenses. It takes skilled IT professionals and careful planning to address this complexity.
Resistance to Change
There is fear among healthcare staff that AI systems will take their jobs or there might be hard work in coping with new technology they are not familiar with. With a lack of training and communication around the reason for the new introduction, resistance will impinge on the success of the system.
Ethics and Legality
The application of AI in making decisions is bringing ethical dilemmas. For instance, if an AI system fails to diagnose a condition accurately, who is liable becomes ambiguous. Still, legal frameworks that will direct such issues are evolving.
Necessity for Regular Updates and Maintenance
AI technology changes rapidly, and thus, systems need to undergo repeated updates to stay current and efficient. Organizations with limited IT resources may incur expensive and time-consuming delays in constantly updating their systems.
Limited Data Quality and Bias
The prime determinant in the efficiency of AI systems is data quality. If input data is not complete, outdated, or biased, the outputs will also be flawed. Addressing these issues requires rigorous data curation and validation processes.
Best Practices for AI-Powered Health Information Management Systems Adoption
Effective utilization of AI-powered health information management systems mainly involves a strategy that incorporates planning and implementation. Following are the best practices to ensure smooth implementation and sustainable success in the long term.
Needs Assessment
Conduct the needs assessment for identification of particular problems that the organization has faced with the present health information systems. Identify the opportunities where the AI is likely to create the highest yield, like reducing error, fast-tracking the process, or enhancing data security.
Select the Best-Fit Solution
AI systems are not just the same. By understanding the decision-making enhancement characteristics of AI, organizations could know where in the actual use of the tools exists a potential of delivering real value. Make your evaluations based on the scalability of the tools, adaptability with existing infrastructure, and the most important point in all- ease of integration. Fit your best solution to the size, budget, and technical capacity of your organization.
Bring on Stakeholders from the Outset
Key stakeholders include administrators, IT teams, and end-users whereby their input is sought early on for ideas around decision making. An early approach ensures buy-in and reduces negative resistance against change as all concerns will have been addressed, and expectations reasonably set.
Invest in Placement Training
AI systems are effective only when operated by capable users. Train users to understand the inner workings of the system, its outputs, and its implementation in day-to-day activities. A periodical refresher training is vital for ensuring users evolve together with the systems.
Prioritize Data Security
Strong security measures should be implemented to protect the sensitive patient information through encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular security audits. Therefore, compliance with HIPAA and other legal requirements should become a central concern.
Start Small, Scale Gradually
Start with a pilot program to validate system functionality with a few end users in a controlled environment. Use the insights gained during these lessons to adjust the implementation path before a full-scale rollout is undertaken.
Unifying Teams
AI implementation involves more than IT; it involves clinicians, administrators, and developers to find synergies, demonstrating how AI enhances decision-making so that the system benefits all user categories.
Constant Performance Monitoring and Tuning
The performance of the system is monitored on a periodic basis and user feedback is solicited. This provides an opportunity to modify and enhance AI systems in correspondence with user feedback over time, thus securing their relevance and efficiency.
Long-Term Maintenance Considerations
There will be a need for continuous AI applications maintenance so as to keep with trends and changing laws. Funding will have to be set aside for software updates, hardware upgrades, and technical support.
Staying true to these best practices will help ensure that healthcare practitioners and tech developers can fully realize the benefits of AI-enabled health information management systems, while at the same time managing any risks which may arise from it.
Conclusion
An AI Hospital-based Information Management System changes the way organizations know how to run their day-to-day activities. From making data accurate and lessening the burdens of business-making to improving patient care, the promise is an entirely transformative experience. Issues do exist: data privacy, costs, and complexities of integrations being some, all calling for a detailed planning and implementation strategy.
To healthcare administrators, operational efficiency while maintaining regulatory compliance is at the heart of the promise of these systems. For the tech developers, innovation and resolution of real-world problems present themselves as a great opportunity. Familiarity with the benefits, anticipation to hurdles, and observance of best practices in using such functions translate into leveraging AI for bettering health care while working towards developing an environment that will work proficiently with the patients.
This is how highly we will use these systems to determine the near future of health care. Properly applied, AI will be that convoluted partner in enhancing health, tackling the rising complications of health information management.