Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a transformative force in healthcare, reshaping how management information systems (MIS) function to enhance patient care. For healthcare administrators, IT professionals, and hospital executives, the integration of AI into MIS isn’t just about adopting new technology—it’s about redefining how hospitals and clinics operate at their core.
This post dives into the ways AI is improving patient care by optimizing Hospital Management Software. You’ll discover how AI-driven tools are reducing administrative burdens, improving clinical decision-making, and ensuring better patient outcomes. We’ll also explore implementation strategies, potential challenges, and real-world examples of AI in action.
Benefits of AI in Healthcare Management
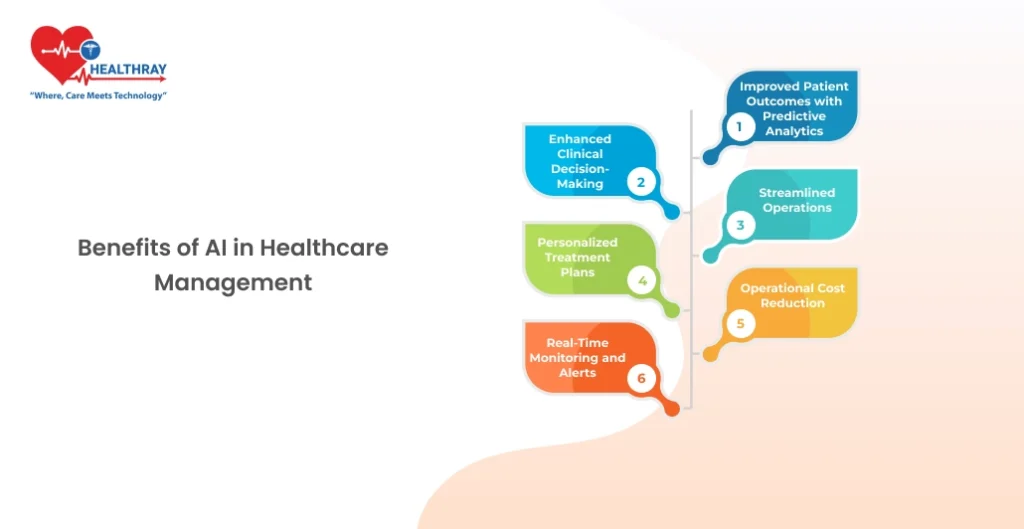
AI is revolutionizing healthcare management systems, delivering a range of benefits that directly impact patient care and hospital efficiency. Below are the key advantages AI brings to healthcare management:
Improved Patient Outcomes with Predictive Analytics
AI-powered predictive analytics helps healthcare providers anticipate patient needs and potential complications. By analyzing historical data and real-time patient information, AI identifies patterns that humans might miss. For example:
- Early detection of diseases, such as sepsis or cancer, allowing timely intervention.
- Predicting patient readmissions, enabling hospitals to take preventative measures.
Enhanced Clinical Decision-Making
AI supports clinicians by providing evidence-based insights during critical decision-making processes. Decision support systems analyze patient data, research papers, and clinical guidelines to suggest treatment options or flag potential risks. This reduces errors and ensures that patients receive the most effective care.
Streamlined Operations
Administrative tasks often consume a significant portion of a healthcare professional’s time. AI automates routine processes, such as:
- Appointment scheduling and follow-ups.
- Claims processing and billing.
- Data entry and recordkeeping. This frees up healthcare staff to focus on patient care rather than paperwork.
Personalized Treatment Plans
AI systems analyze vast amounts of data, including genetics, lifestyle, and medical history, to create personalized treatment plans. Tailored care ensures patients receive treatments best suited to their unique needs, leading to better outcomes.
Operational Cost Reduction
While AI implementation may require an upfront investment, its long-term impact often includes significant cost savings. AI reduces inefficiencies, minimizes wastage, and lowers the likelihood of costly errors, making healthcare more affordable and sustainable.
Real-Time Monitoring and Alerts
Wearable devices and remote monitoring tools powered by AI provide real-time updates on a patient’s health. For example:
- AI monitors vitals and sends alerts to doctors when anomalies are detected.
- Chronic disease patients benefit from continuous tracking, reducing emergency visits.
Implementing AI in Management Information Systems
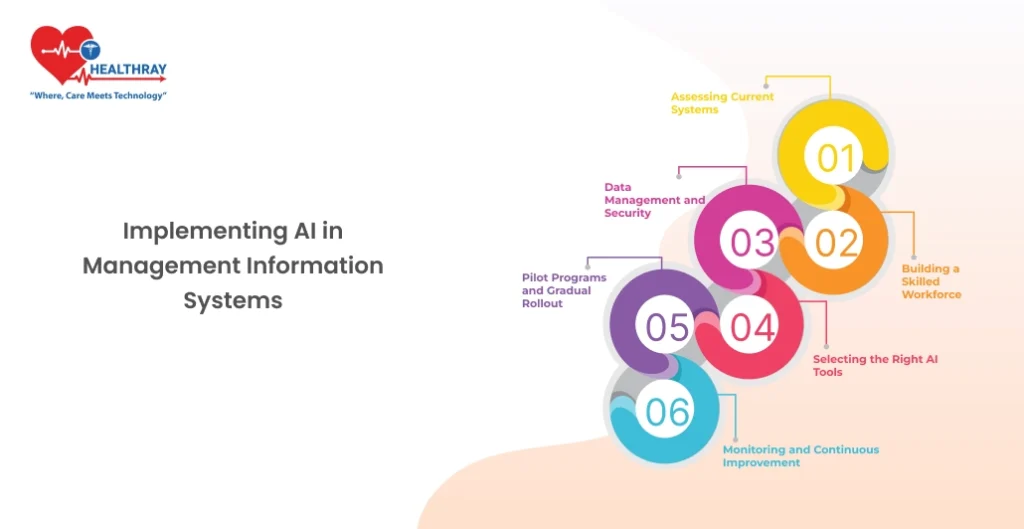
Integrating AI is Transforming Hospital Management Software requires a strategic and well-thought-out approach. This section highlights the key steps and considerations to ensure a smooth and impactful implementation.
Assessing Current Systems
Before introducing AI, healthcare organizations need to evaluate their existing MIS infrastructure. Questions to consider include:
- Are the current systems capable of integrating AI technologies?
- What are the pain points in the current processes that AI can address?
Conducting a thorough assessment helps identify gaps and prioritize areas where AI can deliver maximum value.
Building a Skilled Workforce
AI tools are only as effective as the people using them. Training and upskilling staff are essential for successful implementation. This includes:
- Educating healthcare administrators on AI applications and benefits.
- Providing hands-on training for IT professionals to manage and maintain AI systems.
- Training medical staff to interpret AI-generated insights confidently.
A well-prepared workforce minimizes resistance to change and ensures optimal use of AI systems.
Data Management and Security
AI relies heavily on data to deliver accurate insights. Ensuring high-quality, secure, and well-structured data is critical. Key considerations include:
- Implementing robust data management protocols.
- Adhering to strict privacy laws like HIPAA to protect patient information.
- Using encryption and other security measures to prevent data breaches.
Without secure and clean data, the effectiveness of AI in MIS diminishes significantly.
Selecting the Right AI Tools
Not all AI solutions are one-size-fits-all. Choosing the right tools depends on the specific needs of the healthcare organization. For instance:
- Predictive analytics tools for better patient outcomes.
- Natural language processing (NLP) tools for streamlining documentation.
- Workflow automation tools to reduce administrative overhead.
Collaborating with vendors who understand healthcare needs ensures alignment between AI capabilities and organizational goals.
Pilot Programs and Gradual Rollout
Rushing into full-scale AI implementation can lead to unforeseen issues. Starting with pilot programs allows organizations to:
- Test AI tools in real-world scenarios.
- Identify potential challenges and rectify them early.
- Gather feedback from staff and refine processes.
A phased rollout ensures that the organization adapts seamlessly to the new systems.
Monitoring and Continuous Improvement
AI implementation isn’t a one-and-done process. Regularly monitoring AI systems helps:
- Measure their effectiveness in achieving set goals.
- Identify areas for improvement.
- Keep up with advancements in AI technologies to stay ahead.
Challenges and Considerations
While the potential of AI in healthcare management information systems is undeniable, it comes with its own set of challenges and considerations. Addressing these proactively can help healthcare organizations maximize the benefits while mitigating risks.
High Implementation Costs
AI technologies often require significant upfront investment. This includes the cost of:
- Purchasing and integrating AI systems.
- Training staff to use the new tools.
- Upgrading existing infrastructure to support AI capabilities.
For smaller healthcare organizations with limited budgets, these costs can pose a barrier. Careful planning and phased implementation can help distribute expenses over time.
Data Privacy and Security
AI systems rely on large volumes of patient data, which raises concerns about data privacy and security. Key challenges include:
- Adhering to stringent regulations like HIPAA or GDPR.
- Preventing data breaches and unauthorized access.
- Ensuring anonymization and encryption of patient data.
Robust cybersecurity measures and compliance frameworks are essential to address these concerns.
Ethical Considerations
AI systems are only as unbiased as the data they are trained on. Potential ethical concerns include:
- AI algorithms inadvertently amplifying biases in healthcare data.
- Decisions influenced by AI that might not align with a patient’s preferences.
- Ensuring AI recommendations remain advisory, with clinicians making the final decisions.
Establishing ethical guidelines and regular audits can help organizations address these issues responsibly.
Resistance to Change
Healthcare staff may resist adopting AI due to concerns about:
- Job displacement or reduced roles.
- Difficulty in learning new technologies.
- Trust in AI-generated insights over human expertise.
Building awareness about the collaborative role of AI in enhancing, not replacing, human decision-making can reduce resistance. Hands-on training and open communication are crucial here.
Integration Challenges
AI systems must integrate seamlessly with existing management information systems. Challenges include:
- Compatibility issues with legacy systems.
- Complexities in data migration and standardization.
- Downtime during implementation, which can disrupt operations.
Collaborating with experienced vendors and creating a robust integration roadmap can help navigate these hurdles.
Measuring ROI
Healthcare executives often struggle to quantify the return on investment (ROI) from AI systems. Challenges include:
- Delayed outcomes, such as improved patient care, which may take time to reflect in measurable metrics.
- Difficulty linking financial savings directly to AI interventions.
- Setting appropriate benchmarks to evaluate AI performance.
Defining clear objectives and KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) at the outset ensures ROI evaluation aligns with organizational goals.
Evolving Technology Landscape
AI is a rapidly advancing field, and tools implemented today may become obsolete in the near future. This creates a need for:
- Continuous learning and adaptation.
- Staying updated with the latest AI advancements.
- Regularly upgrading systems to maintain relevance.
Case Studies: Real-World Applications of AI in Healthcare Management
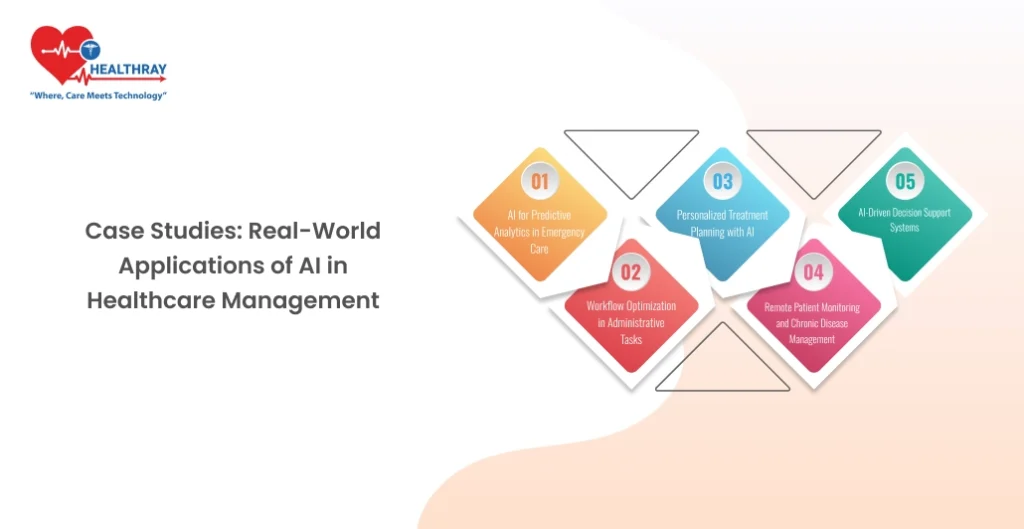
Examining successful implementations of AI in healthcare management provides valuable insights into its potential and practical applications. Below are examples where AI has made a tangible impact.
AI for Predictive Analytics in Emergency Care
A major HMS Software implemented AI-powered predictive analytics to manage emergency department workflows. By analyzing historical data and real-time patient information, the AI system predicted patient admission probabilities. This allowed staff to:
- Allocate resources effectively.
- Reduce wait times for critically ill patients.
- Improve overall patient satisfaction scores.
The hospital reported a 20% reduction in patient wait times and smoother emergency department operations.
Workflow Optimization in Administrative Tasks
A large healthcare provider integrated AI into its management information system to streamline administrative processes, such as appointment scheduling and billing. The system used natural language processing (NLP) to:
- Automate data entry from patient forms.
- Flag inconsistencies in insurance claims for quicker resolution.
- Optimize appointment scheduling to minimize gaps in the physician’s schedule.
This resulted in a 30% reduction in administrative overhead and faster billing cycles, improving cash flow and operational efficiency.
Personalized Treatment Planning with AI
A cancer treatment center used AI to analyze patient data, including genetic profiles and treatment histories, to create personalized care plans. The AI system suggested the most effective treatments based on:
- Tumor characteristics.
- Likely responses to specific therapies.
- Potential side effects.
Patients experienced improved outcomes, with a 15% increase in treatment success rates and fewer adverse effects.
Remote Patient Monitoring and Chronic Disease Management
A regional health system deployed AI-enabled wearable devices to monitor patients with chronic conditions such as diabetes and heart disease. These devices:
- Sent real-time alerts to physicians about abnormal health trends.
- Suggested lifestyle adjustments based on data analysis.
- Reduced the need for frequent in-person check-ups.
The program led to a 25% decrease in hospital readmissions for chronic disease patients, saving the health system millions annually.
AI-Driven Decision Support Systems
A university hospital implemented an AI decision support system for ICU physicians. The system analyzed real-time patient data and provided insights into:
- Medication dosages.
- Potential complications.
- Early warning signs of sepsis.
By adopting this system, the hospital reduced ICU mortality rates by 18%, highlighting the life-saving potential of AI.
Future Trends in AI for Healthcare Management
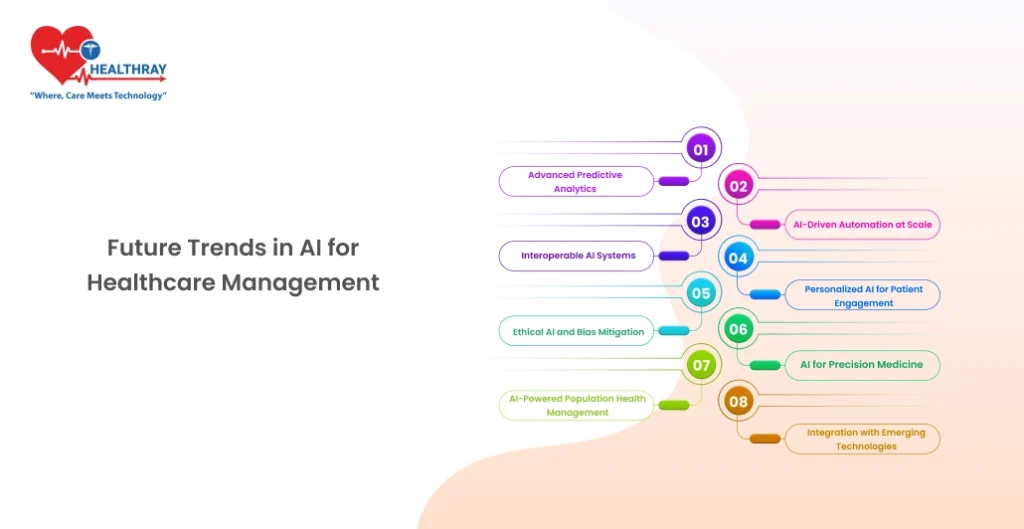
The field of AI in healthcare management is evolving rapidly, offering exciting possibilities for the future. Here’s what healthcare administrators, IT professionals, and hospital executives can expect in the coming years.
Advanced Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics will continue to evolve, becoming more precise and widespread. Future systems may:
- Predict outbreaks of diseases at a community level using population data.
- Anticipate long-term patient health risks for proactive intervention.
- Enable personalized wellness plans based on predictive trends.
AI-Driven Automation at Scale
Routine tasks like medical coding, claims processing, and documentation will see deeper automation. For example:
- AI systems could handle end-to-end billing processes with minimal human intervention.
- Virtual assistants might assist patients with queries, reducing the workload for administrative staff.
These advancements will free up healthcare professionals to focus more on patient care.
Interoperable AI Systems
Currently, integrating AI with existing systems is a challenge due to compatibility issues. Future AI systems are expected to be more interoperable, allowing:
- Seamless data exchange between different platforms and devices.
- Better collaboration across departments and organizations.
- Unified patient records accessible across providers.
This will enhance the quality and consistency of care delivery.
Personalized AI for Patient Engagement
AI is poised to transform how patients interact with healthcare systems. Future applications might include:
- Virtual health assistants offering personalized health tips and reminders.
- AI-driven mobile apps to monitor and manage chronic conditions.
- Real-time health coaching based on wearable device data.
Engaged patients tend to experience better outcomes, making this a key area of focus.
Ethical AI and Bias Mitigation
As AI adoption increases, so does scrutiny over ethical issues and biases in algorithms. Future trends will likely focus on:
- Transparent AI models that are easier for humans to interpret.
- Development of unbiased datasets to ensure equitable outcomes for all demographics.
- Enhanced oversight to prevent unethical use of AI.
AI for Precision Medicine
AI will further enable precision medicine by analyzing data sets from genomics, biomarkers, and medical imaging. This trend will lead to:
- Tailored treatment plans for conditions like cancer and rare diseases.
- Improved accuracy in predicting treatment responses.
- Faster drug discovery and clinical trial processes.
AI-Powered Population Health Management
Healthcare providers will increasingly use AI to address broader health trends. This includes:
- Managing resources during pandemics or large-scale health crises.
- Identifying social determinants of health for targeted interventions.
- Improving access to care for underserved populations.
Integration with Emerging Technologies
AI will combine with other cutting-edge technologies like:
- Blockchain for secure, decentralized health records.
- 5G connectivity for real-time data transmission in remote patient monitoring.
- Augmented Reality (AR) for enhanced training and telemedicine experiences.
Preparing for the Future
Healthcare organizations should begin laying the groundwork by:
- Staying updated with emerging AI technologies.
- Building flexible systems that can adapt to future advancements.
- Cultivating a culture of innovation to encourage adoption.
Conclusion
Artificial intelligence is redefining the way hospital software operate. From predictive analytics that foresee patient needs to workflow automation that reduces administrative burdens, AI is a game-changer for healthcare administrators, IT professionals, and hospital executives.
While the journey of AI integration presents challenges such as high costs, data security concerns, and ethical dilemmas, the benefits far outweigh these hurdles. AI offers tangible improvements in patient outcomes, operational efficiency, and cost savings. Real-world examples and emerging trends further highlight its transformative potential in creating a more responsive, personalized, and efficient healthcare system.
Healthcare organizations that embrace AI as a strategic partner, rather than just a tool, will be better positioned to deliver exceptional patient care. As we look to the future, the continued collaboration between human expertise and AI innovations will shape a new era of healthcare excellence.





