Electronic health records have revolutionized healthcare delivery. They are much more than the digital version of paper charts; they have become a cornerstone in modern healthcare. EHRs store accurate and updated information about patients that can be instantly accessed by healthcare professionals, thus enabling them to make quick decisions with minimal chances of errors and facilitating better care.
But that is not all: EHR software improves patient outcomes and advances the efficiency of both hospitals and clinics. They decrease paperwork, hence streamlining workflows to save time for both the provider and administrator. This post breaks down exactly how EHRs achieve these benefits and what they mean for the future of healthcare.
How EHR improves Patient care?

EHR systems manage the health-related information of patients digitally. Consider them a centralized database that functions in place of paper records but offers so much more. They reflect a patient’s medical history comprehensively, including diagnoses, medications, test results, and even imaging.
Unlike older records, EHRs are created for access. Any health provider accesses the patient data anywhere on an authorized device, clinic, or hospital or in a remote place. It enables communication to take place without disruptions within the different departments and between healthcare organizations.
Key features of EHRs include
Patient History Management: All chronic conditions, medications, and previous treatments are kept on record.
Alerts and Notifications: Notification related to drug interactions or allergies.
Integration with Diagnostic Tools: Lab results are ready in real time, along with images and other important data.
Real-time information sharing: enables specialists and care teams to work together efficiently.
EHRs represent the shift from paper charts to integrated, digital systems that improve quality of care and pave the way for innovations such as telemedicine and personalized healthcare.
Impact on Patient Outcomes

EHRs are changing the way healthcare providers handle patient care. Fundamentally, they improve patient outcomes because they ensure that the right information about the patient is communicated accurately in real-time to a healthcare professional. Here’s how:
Complete and Accurate Information
EHRs consolidate all the relevant information about a patient in one place-so there’s no fear of missing any important information relating to previous diagnoses, allergies, and medication history. With easy and accurate access to this information, errors are minimized while decisions can be made much quicker by providers.
Medical Errors Reduction
EHRs consolidate all relevant patient information in one place; there is no fear of missing out on important information related to past diagnoses, allergic history, and medication history. With easy, accurate access to the information, errors are minimal, while providers arrive at decisions much faster.
Better coordination between providers
Health care is often provided by teams. With EHRs, specialists, primary care physicians, and other providers can simultaneously have access and update patient information. Collaboration of this nature strengthens treatment plans, eliminates redundant tests, and maintains continuity in care.
Increased preventive care
For example, EHRs can be programmed to monitor screenings, vaccinations, and follow-up visits. Automated reminders are particularly helpful for ensuring that patients receive preventive care. This is most valuable in the management of chronic illnesses such as diabetes and heart disease.
Support for Evidence-Based Care
Clinical guidelines and decision-support tools are integrated into workflows in EHRs, enabling practitioners to provide the best care based on available research and current standards. This should lead to better outcomes and increased satisfaction among patients.
EHRs make the care more precise, proactive, and personalized to the patient. In fact, these have become an essential part of ensuring quality healthcare in today’s fast-moving world.
Operational Efficiency Improvement
While improving patient care, EHRs also revolutionize the operational aspects of providing healthcare. EHRs make healthcare systems more efficient and less error-prone by streamlining workflows and diminishing administrative tasks. Here’s how:
Workflows Simplified
EHR automates many time-consuming activities related to updating patient records, appointment scheduling, and prescription management. Thus, it enables healthcare practitioners to focus more on patient care rather than doing paperwork. To the hospital administrators, it simplifies resource allocation and managing the staff.
Reduction in Paperwork
Gone are the days of sifting through stacks of paper records. EHRs store everything digitally, reducing physical file management burdens. This saves time and reduces costs related to printing, storage, and retrieval.
Faster Access to Information
EHRs also allow healthcare professionals to access a patient’s record in just a matter of seconds, no matter the location. This is very important during emergency situations where time can mean life or death.
Improved billing and coding accuracy
The EHR simplifies the billing process by incorporating medical coding directly into the system, thus minimizing claims-submission errors and speeding up reimbursements. There are fewer disputes over bills, and cash flow improves within hospitals and clinics.
Data-Driven Decision Making
EHRs have made it so easy to analyze data on a healthcare organization. Administrators can, therefore, track a trend in patient outcomes by monitoring resource utilization and identifying where improvement is needed. The insights further enable smarter decision-making, helping prioritize investments in care delivery.
Support for Remote and Collaborative Care
EHRs have enabled care providers to coordinate care between facilities and even from a distance. Through telemedicine platforms integrated with EHRs, access to patient records is assured for every virtual consultation, hence making remote care as effective as visits in person.
Compliance to Regulatory Standards
EHRs themselves are designed with healthcare laws like HIPAA in mind. There are automated audit trails and secure handling processes for data, besides built-in tools for compliance. Administrative loads to maintain compliance have thus been considerably reduced.
In essence, EHRs streamline operations in health facilities by saving time and reducing costs. This saves processes from being derailed; thus, allowing hospitals and clinics to get on with what really matters-providing good care.
Implementation Challenges of EHR
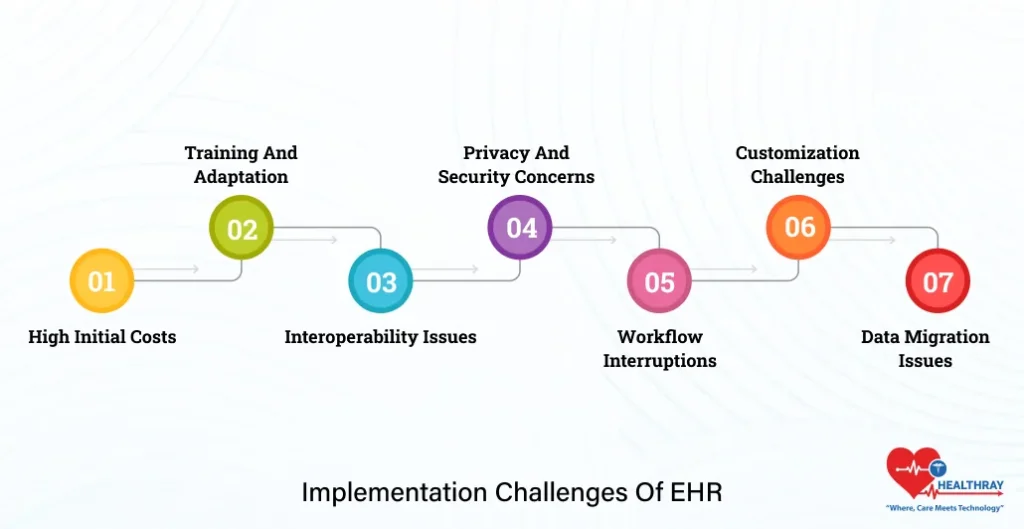
However, like all tools, EHR software does have a set of challenges. It requires a lot of effort, resources, and flexibility to set up the system. The first step toward surmounting these challenges is identification.
High initial costs
The implementation of EHRs costs significant sums, including acquisition of the software, equipment upgrading, and maintenance; hence it becomes a financial challenge to the small practices. There are, however government incentives and funding that help diminish these financial constraints.
Training and Adaptation
Health care providers and staff face significant learning curves when transitioning to EHRs. Training sessions take a lot of time and resources, and adjusting to new workflows temporarily disrupts day-to-day operations. Resistance to change can be common among seasoned professionals.
Interoperability Issues
Not all EHR Health Systems are created equal, and due to a lack of standardization, such systems from other vendors will not communicate effectively with one another. This is a problem in the seamless transfer of data between healthcare providers and facilities, actually limiting the full potential of EHRs.
Privacy and Security Concerns
Because very sensitive data of the patients is maintained digitally, cybersecurity is a huge concern these days. A data breach would imply loss of patient trust and a financial penalty due to non-compliance with certain regulations. This will require more investment by organizations in the security of the data.
Workflow Interruptions
EHR systems can temporarily affect workflows. Documentation and patient care by the providers may be temporarily delayed due to the new nature of the system. If an EHR is not well implemented, efficiency may even be negatively affected if it is not adapted to the nature of the organization.
Customization Challenges
Healthcare facilities have very unique needs, and often an off-the-shelf EHR solution will not meet all of those needs. It can be expensive and time-consuming when trying to tailor the use of the EHR system to specific practice needs. Frustration could build if an EHR system is not appropriately tailored: either features that are needed aren’t present or vice versa.
Data Migration Issues
Data transfer from paper-based records or legacy systems to EHRs is an extremely complex task. Incorrect migration leads to incomplete or inaccurate information on patients, hence weakening the effectiveness of the system.
Future Trends in EHRs
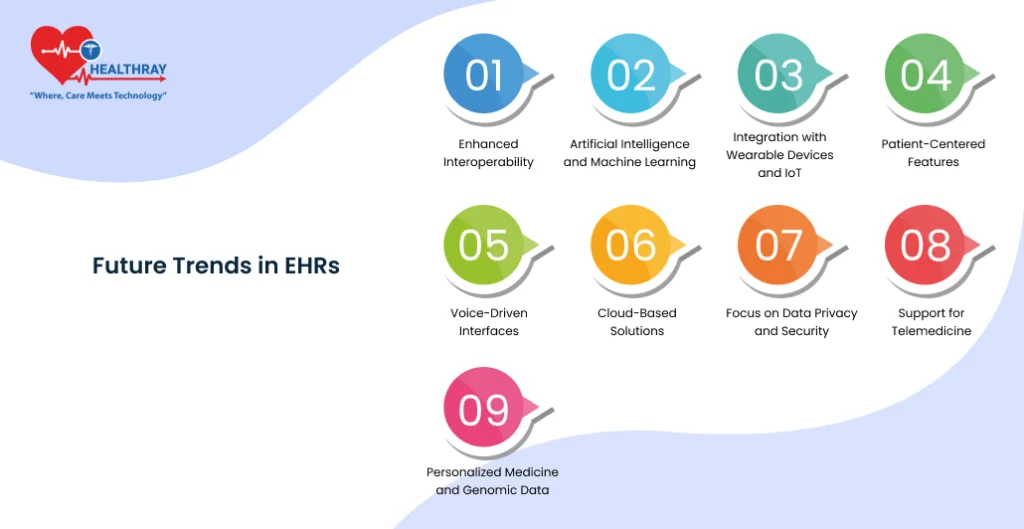
The future of EHR systems shines bright and full of possibilities. Technology will continue to change; so will EHRs, overcoming current challenges while offering more value to healthcare providers and their patients. Here’s a look at the trends shaping the next generation of EHRs:
Improved interoperability
The biggest challenge regarding EHRs nowadays is the lack of smooth interaction between the systems. Future EHRs would overcome this challenge by focusing on standardized protocols for data exchange, such as FHIR. This will lead to easier collaboration across facilities and ensure that patient data is available where it is needed.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI will definitely alter the direction of EHR regarding predictive analytics and decision support. Algorithms go through massive data sets, identifying patterns in data to forecast outcomes for a specific patient and make recommendations on evidence-based, individualized interventions. With machine learning, such administrative tasks as coding and documentation can also be automated, saving time and reducing errors.
Integration with Wearables and IoT
Wearable health devices and IoT will most likely increase the functionality of EHRs. Such wearables as fitness trackers, smartwatches, and home monitoring devices can feed data to EHRs in real time. It gives healthcare providers a more panoramic view of the status of a patient’s health even outside the clinical setting.
Patient-Centered Features
Future EHRs will increasingly be oriented to engage the patient through more user-friendly portals. These platforms allow patients to access their medical records, schedule appointments, request prescription refills, and even directly communicate with providers. Greater transparency and availability encourage active patient participation in their care.
Speech-driven Interfaces
It also involves speech recognition technology, and it is gradually being applied in EHR systems to easily interact with providers. In this regard, clinicians are able to dictate rather than type long notes about observations, diagnoses, or treatment plans as a possible way of saving precious time through reducing documentation fatigue.
Cloud-Based Solutions
Cloud-based EHRs are now gaining more traction for scalability, financial efficiency, and accessibility. They reduce the need for expensive on-site servers and enable providers to access patient records from anywhere securely.
Focus on Data Privacy and Security
With increasing concern about data breach, the future EHR will have advanced security features, comprising better encryption, multi-factor authentication, and enhanced cybersecurity applications. These would make it highly reliable to instill faith among patients and comply with ever-changing regulatory standards.
Support for Telemedicine
With the rising popularity of telemedicine, EHRs will be pivotal in integrating virtual care into traditional health care. Future systems will connect telehealth platforms with patient records for seamless transitions between virtual and in-person visits.
Personalized Medicine and Genomic Data
Integration of genomic data into EHRs will open the door for personalized medicine. Providers will be able to create treatment and prevention plans more personalized by analyzing the genetic information in context with their patient’s medical history.
Conclusion
EHRs have been transformative for modern healthcare, both in terms of improving patient outcomes and operational efficiency. They allow practitioners to have updated, comprehensive information about the patient on demand in real time to make informed decisions, avoid errors, and co-operate more effectively. EHRs iron out wrinkles in workflows for administrators in hospitals, reducing associated costs while raising the level of compliance to regulatory standards. Advances in technology are winning against most challenges, apart from those of high implementation costs and data privacy. Backed by emerging trends in interoperability, integration of AI, and personalized medicine, which have transformed the face of healthcare delivery, the future of the Hospital Management System does look bright. Indeed, one fact has become clear for healthcare professionals, hospital administrators, and EHR solution providers: embracing EHR technology is no longer optional; this is a move toward better care and smooth operations for a healthy future.




