The diversity and volume of work that laboratories handle today have resulted in the majority becoming busier than they have ever been, with complex workflows, countless data points, and stringent regulatory requirements. In such cases, trying to keep everything in working order either manually or through outdated software only facilitates errors, waste, and compliance risks for the laboratory. This is where the Laboratory Information System (LIS) software appeared in the picture-to change entirely how laboratories function, automate their workloads, centralize their data, and therefore increase accuracy.
The Laboratory Information System offers a partner to lab managers and health administrators in optimizing their operations. Understanding an LIS’s value and capabilities gives software developers involved in the building and integration of Laboratory Information Management System insight into why it has gained such popularity. This article focuses on how LIS software answers the urgent demands of labs that exist today, gains from the perspective of various interested parties, and key features to consider when it comes to the adoption of LIS.
Understanding Lab Information System
A Laboratory Information Management System (LIMS) is a software application for managing lab data, workflows, and processes, bringing order to the highly complex and diverse tasks with which labs contend each day. Unlike general data management systems, LIMS is designed specifically for laboratory settings. This includes data entry, sample tracking, workflow automation, and regulatory compliance management.
The terms “Laboratory Information System” (LIS) and LIMS are often used interchangeably. However, it is worthwhile to clarify a distinction: Laboratory Systems is more commonly used in healthcare for managing patient-related data, while LIMS is a more widespread term referring to collar sample management, process control, and data analysis. This understanding aids labs in choosing the software that can suit them best.
For lab managers, a LIMS creates transparent visibility into lab operations, allowing easier tracking of samples, inventory management, and data integrity. To this, the software developers building LIMS software extract great benefits in understanding the LIMS’s core functionalities in terms of laboratory instrument interoperability and customizability to fit varied lab settings. On that note, the next section would describe the specific benefits of LIMS to lab operations and data management.
Benefits of LIMS in Modern Laboratories
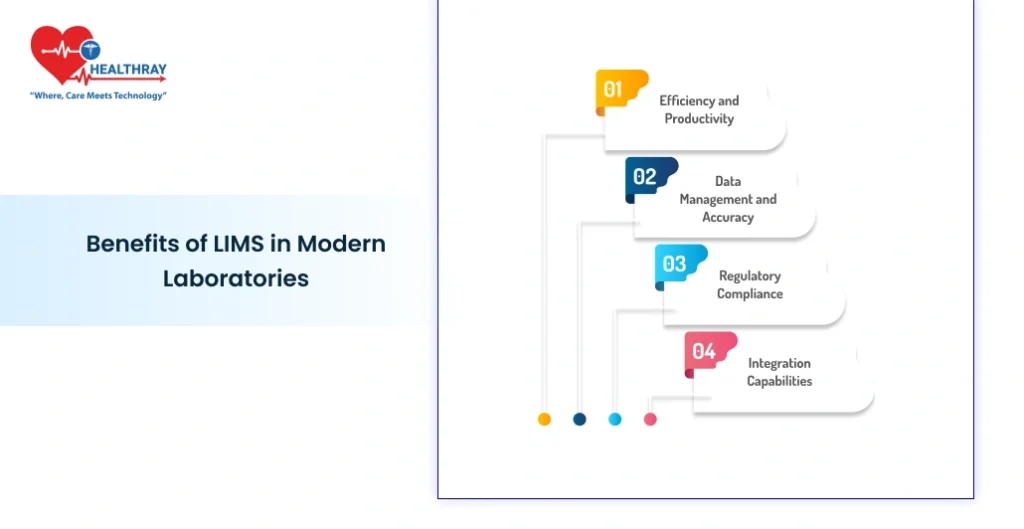
LIMS include achievements extending beyond data organization. LIMS aids the laboratory in substantially increasing operational efficiency, data accuracy, and compliance.
Efficiency and Productivity
Among the most prominent advantages of LIMS is its functionality in automating otherwise manual tasks. This allows personnel to spend more time on mission-critical activities rather than the mundane tasks of data entry. A laboratory may set up workflows that route samples automatically through various stages, sending alerts to staff as to when action is required. This helps to minimize human error and increases speed of turnaround, thereby guaranteeing that results get to the stakeholders faster and productivity has been pushed upward.
Data Management and Accuracy
While applying any scientific process, data is the lifeblood of laboratory operations. LIMS provides a consolidation of stored data; thus, it readily provides information on a sample, a result, and a historical record in one place. They also standardize and basically provide the matrix value of data entry and management, which helps to ensure that data accuracy and traceability are also being maintained. Any updates or corrections are registered, which provides an audit trail, especially useful when a lab has to look back at a result or prove its integrity.
Regulatory Compliance
Compliance with industry regulations is crucial, particularly in highly regulated sectors such as healthcare and pharmaceuticals. The LIMS simplifies compliance by ensuring that labs continuously follow standard operating procedures (SOPs) and generating a traceable record for each sample or test conducted. Irrespective of whether it is ISO, CLIA, or FDA, it guarantees the records are complete, accurate, and accessible for any audit purpose.
Integration Capabilities
LIMS are able to integrate through the many laboratory instruments and cross-software to provide a fluid data stream between the systems. This action of integration cuts down the redundancy of data entry and the possibility of error occurring when transferring information from device to device. For instance, when LIMS integrates with laboratory instruments, data will be electronically captured and recorded, thus enhancing accuracy and saving time. This capability within LIMS offers developers a level of flexibility allowing customization made to suit a lab’s specifics in regards to its equipment and operational requirements.
Technical Insights For Software Developers

It is critical for software developers in Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS) to grasp the technical architecture and integration approach in order to construct those systems that fit to the current needs in a laboratory. LIMS is more than a commercial data management system; it imposes on itself flexibility, security, and scalability to suit the diversified needs of laboratories.
System Architecture and Design
One indexing best-proportioned design of LIMS will have followed a modular architecture. It is easier to update individual components on their own without having to renegotiate on the entire system. It enhances scalability, allowing labs to add functionalities as necessity burgeons. Developers using microservices and containerization may discover increased flexibility, offering strong performance even in changing laboratory conditions.
Customization and Scalability
No two laboratories are alike, and therefore, LIMS must be able to accommodate differing workflows and user preferences. Building a customizable LIMS offers laboratories the opportunity to set up workflows, reports, and dashboards relevant to their processes.
This customization tends to extend to user roles and permissions, and as such, ensures confidentiality of sensitive information and restricts accessibility to approved personnel. For scalability, cloud solutions are progressively becoming the trend, allowing laboratories to change their LIMS use and storage based on real-time demand.
Integrated LIMS
It works across a gamut of laboratory instruments and software with databases. With the integration, data exchange between the two systems is seamless, reducing the necessity for manual data entry and thus decreasing opportunity for errors. The issue of LIMS developer compatibility of some common lab equipment and EHR systems would be a distillation in the healthcare context.
This is, APIs and middleware could help to a great extent in securing a data exchange, besides providing the means to LIMS developers for linking these systems for third-party or legacy software use.
Data Security and Compliance Features
As LIMS deals with sensitive data, security becomes a burning concern. Developers have to incorporate such features as encryption, user authentication, and access controls for the protection of data. Compliance features, too, should restrict such things as audit trails and data versioning, a must in regulations-heavy industries. Secure cloud storage for data would go a long way in enhancing data protection, along with regular updates to all security systems to be in line with respective compliance standards such as HIPAA for healthcare and ISO for laboratories.
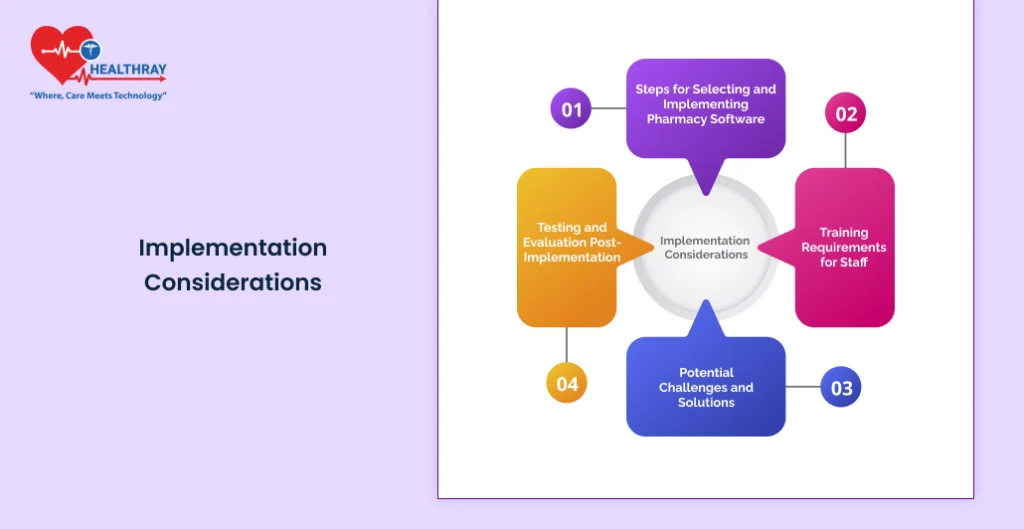
Implementation Considerations
Implementing a laboratory information management system (LIMS) requires a good deal of planning so it fits the operational needs of given laboratories while making a smooth changeover for their employees. Implementation, as noted from deciding on laboratory needs and cost implications, is pivotal to LIMS’s success.
Assessing Laboratory Needs
A lab manager should conduct a needs assessment prior to LIMS selection to identify the specific functions and features needed in the lab. This looks at parameters such as the sample load of the lab, regulatory needs, reporting expectations, and data management issues. The selected LIMS should fill this operational need by way of automation, regulatory compliance, or data analytics, whichever one of these becomes paramount.
Cost Implications and ROI Analysis
LIMS implementation constitutes a considerable amount of money, and the lab managers must know about its return on investment (ROI). Besides upfront software and hardware costs, the long-term costs borne by the lab may include maintenance, updates, and even staff retraining. Largely, however, this ROI justifies the costs. LIMS reduces errors, enhances productivity, improves data management-all of which saves time and resources. Lab managers should quantify these potential benefits against costs to ensure that the investment fits the lab’s budget and goals.
Training and Support for Successful Adoption
Adoption of LIMS is dependent on extensive user training. This can range anywhere from training all levels of personnel involved with the software, including its functional areas, data entry and reporting, to other workflow management functions. Further-on-the-job support options, such as helpdesk and dedicated support teams, are equally invaluable to troubleshoot on live issues that emanate after the implementation. Confidence and competence among staff translate to a reduced learning curve and thorough maximization of the LIMS.
Long-Term Maintenance and Updates
The focus of a LIMS is updated regularly in sync with regulatory changes and advances in lab technology. Maintenance generally means application updates, data backup, and installation of security patches. It is good to have a maintenance plan in place, including proposed schedules to be made by lab management itself or an IT team to properly check maintenance from the services offered by the LIMS provider. Working on this provides an opportunity to tackle the need for sustaining LIMS functionality and maintaining integrity of the data across its life span.
Case Studies
The stories of LIMS projects in action highlight the many benefits and best practices of using LIMS in various laboratory settings. They also provide a window into the experimental world of laboratories-most of them less than perfect-by which those have managed to overcome common pitfalls and create some obvious benefits from using the LIMS.
1. Case Study: Improving Efficiency in a Clinical Lab
Sample tracking and data entry have delayed the processes of a mid-sized clinical lab, making it unsustainable in terms of data accuracy. With the installation of a LIMS, all kinds of automatic sample logging and tracking have to a great extent reduced errors with faster turnaround time by 30%. Central data storage created access for all staff members to test results and reports instantaneously, engendering better collaboration and productivity. It also positioned the LIMS as a compliance instrument to healthcare regulations, facilitating audit preparation much faster and accurately.
2. Case Study: Ensuring Compliance in a Pharmaceutical Lab
Pharmaceutical labs are required to ensure FDA compliance and to be able to provide an audit trail for every sample and every process. The LIMS not only allowed for increased standardization of processes but also required LIMS to become an automated record-keeping system with a well-defined history for every test and sample. For the LIMS audit trail, this quick generation of reports for regulatory audits saved significant time and effort. Conversely, this assurance of compliance freed the lab of regulatory headaches and allowed focus on research.
3. Case Study: Integration in a Multi-Location Research Lab
A set of research labs operating internationally needed an operational solution for better data sharing and collaboration through their sites. Data sharing across sites has now become a simple task since the implementation of cloud-based LIMS, allowing researchers to have real-time access to new insights and updates. The LIMS integrated with various lab instruments across locations, reducing the need for manual data transfer. This approach has proven to save time, lessen data discrepancies, and ensure uniform approaches across all sites.
4. Case Study: Improved Data Security in a Genomic Laboratory
A genomics laboratory dealing with responsible genetic data considered information security among the most critical factors in its requirements on the LIMS. After LIMS implementation equipped with encryption and multi-factor authentication, the laboratory greatly reduced the risk of a data breach. In addition, compliance of the system to HIPAA standards provided the confidence that the data protection mechanism ensured patient data, as well as research data, remained secured. This level of security did not only protect sensitive information but also augmented the credibility of the laboratory with partners and clients.
Conclusion
Laboratories face growing demands today for accuracy; speed in processes; and adherence to regulatory compliance. A Laboratory Information Management System (LIMS) has become indispensable for all these reasons. Automated workflows, centralized data, maintained compliance, and seamless integration with other lab systems are what Hospital Management System software has been doing for laboratories. The advantages extend to all entities-from lab managers who want streamlined operations to healthcare administrators ensuring that everything is up to standard and even to the software developers who have built flexible, secure options.
Choosing a good LIMS allows laboratories to take increasing workloads with accuracy and speed, thereby improving the quality and increasing productivity in the lab. For any lab evaluating a LIMS option, understanding functionality, integration, and implementation requirements will encourage a mind shift in day-to-day operations.