Introduction
The healthcare industry is one of the fast changing segments that bring with them the effects of digital transformation. As current hospitals advance their sophisticated management systems, the aspect of patient care will surely be streamlined and improved. Modern HMS is an integrated state-of-the-art platform not only managing the patient record but it allows more efficient workflow, greater security of data, and maximized effective care for patients.
This was not overnight, however. It has been in the last few decades where there have arisen tremendous interest for faster handling of patient information, accuracy, and security. The modern Hospital Management System solutions respond to this need by making use of tools such as AI, IoT devices, and even cloud-based platforms. This helps healthcare providers gain real-time access to data, coordinate care, and make better decisions in the practice.
Key Features of Modern Hospital Management Systems
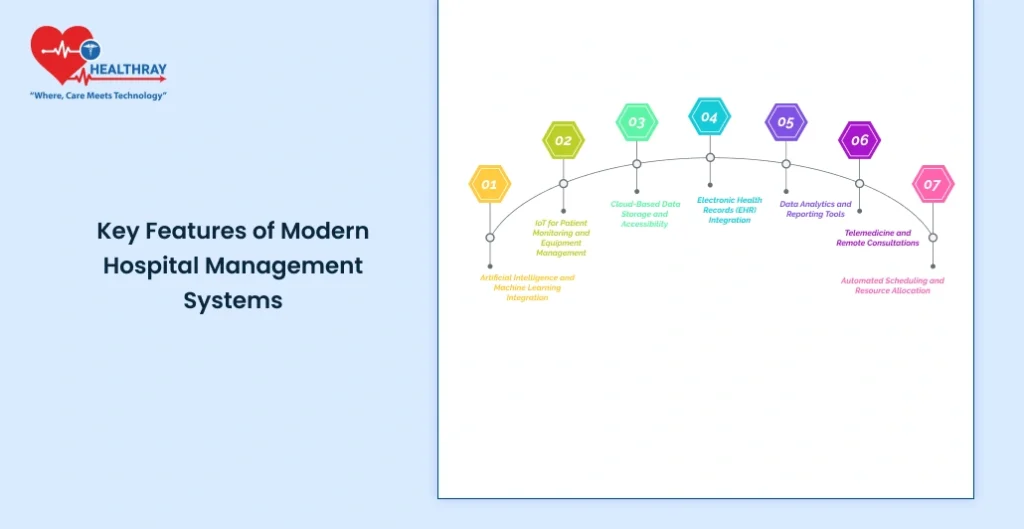
Modern hospital management systems are no longer just about recording information; instead, they have evolved to be a group of sophisticated tools to sustain everything from patient care to work in the back office. The following represent some of the key features that make these systems absolutely indispensable in today’s health environment:
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Integration
It’s rather obvious that artificial intelligence and machine learning are the backbones of today’s HMS platforms. AI will help identify some not very obvious patterns within patient data, assist with faster diagnosis and personalized treatment plans. Predictive capabilities of machine learning can be used to make predictions about patient outcomes based on historical data for the help of doctors and specialists. Resource management will also enhance through these technologies; these can predict infloods of patients and optimize the staff deployment.
IoT for Patient Monitoring and Equipment Management
The Internet of Things (IoT) has brought vast improvements in patient monitoring and equipment tracking. The IoT devices can monitor patient vital signs at all times and feed the information directly into the hospital management system. This automatically diminishes the requirement for manual recording and allows for real-time monitoring, which is critical for risky patients. Equipping the management will ensure the tracking of usage and availability of medical devices so that such vital resources are accessible quickly when needed.
Cloud-Based Data Storage and Accessibility
At the same time, cloud technology in healthcare does provide secure, scalable, and easily accessible data storage options. Cloud-based HMS allows the storage of patient records and hospital data securely online and is accessible by authorized personnel from anywhere. This would prove to be quite helpful for multispecialty hospitals with branches at various locations because the doctors and specialists require immediate access to the records to coordinate proper treatment. The data would also be backed up, so it is well protected from damage due to some physical cause or local technical malfunctions.
Electronic Health Records (EHR) Integration
A current HMS is incomplete without EHR integration. EHRs are data storage of a patient’s medical history, laboratory tests, medications, and lots more, providing a structured view of patient health. By using the features of electronic health records, detailed information about the patients will be retrieved, thus minimizing documentation time and reducing the risk of errors. Furthermore, this feature would allow better coordination between departments and enable healthcare providers to make informed treatment decisions.
Data Analytics and Reporting Tools
The data analytics tools of HMS enable the analysis of trends regarding patients, treatments, and operations based on results. This type of information can be used by administrators to make informed decisions based on data to enhance the quality of care received by patients and lower costs. Reporting tools support performance metrics, such as patient discharge times, bed occupancy rates, and staff productivity. Reports can be tailored to help in day-to-day management as well as long-term strategic planning by administrators.
Telemedicine and Remote Consultations
Another exciting feature of the modern HMS is wider access to healthcare, especially among the patient population in remote areas. Integration of telemedicine into the HMS enables patients to visit doctors through video calls, get prescriptions, and follow up from their homes. The technology significantly improves patient satisfaction, as it minimizes live visits to the facilities only among those patients who will be best treated in person.
Automated Scheduling and Resource Allocation
HMS automation tools make scheduling easier. By performing this, automated tools manage appointment scheduling, surgeries, and the allocation of any other resource such as operation rooms or medical equipment. Automated scheduling reduces conflicts and minimizes patient waiting times and optimizes resource usage within the hospital. Hospital management systems also free up time for healthcare staff through schedule optimization that focuses more on patient care.
Enhancing Patient Care Through Digital Systems
Patient care is the heart of every healthcare facility. Modern HMS improve this kind of care; thus, it is central to system integration using modern digital tools-ways of exchange of information, coordination of care, and, basically, how the patient experiences healthcare services. Here’s a closer look at how digital systems contribute to enhanced patient care:
Streamlined Patient Records and Information Flow
One of the most important changes that HMS brings with it is centralized, accessible patient information. This means all sorts of patient data: medical histories, lab results, medication records, and treatment plans-all are located in one system and accessible everywhere. This saves one from using physical paperwork as well as the dangers of misplaced or outdated information. In turn, doctors and nurses can provide timely, informed care without delay in accessing critical information.
Facilitating Telemedicine and Remote Consultations
Telemedicine is one aspect of healthcare that has become part of the system since it touches many places where the physical availability of healthcare facilities may be relatively scarce. Therefore, HMS provides integrated telemedicine functionality that enables a doctor to do virtual consultations with his or her patients. This has proved to be very useful for follow-up care, routine checkups, and non-acute consultations. Telemedicine brings greater convenience to the patient, a reduction in overcrowding in hospitals, and, therefore, guaranteeing systematic care for high-risk or remote patients.
Personalized Treatment Plans with Data Analytics
HMS will utilize its analytical power to analyze the health metrics of patients and advice them appropriately based on their health requirements. HMS discovers patterns concerning various health metrics like blood pressure flux or flux in glucose levels and supports in planning specialized treatment schemes. Personalization ensures better outcomes for patients since it provides care based on varied needs and individual patient responses by modifying treatment for the specific patient.
Efficient Coordination Among Healthcare Providers
Patients’ care is often a multi-professional activity. In HMS, for instance, all departments can access updated records for patients ensuring that specialist, primary care physicians, and nursing staff are coordinated with no gaps in the communication between them. Thus, any health care professional involved in managing patient care is always up-to-date. This is essential for safe quality care.
Automated Alerts and Reminders for Patient Monitoring
The HMS can also automate alerts and reminders of the critical tasks such as administration of medication, monitoring vital signs, and scheduled tests. For example, the system can automatically send reminders to the nursing station or the on-duty doctor whenever a patient’s heart rate or blood pressure moves out of the designated range. This preventative monitoring prevents potential health crises and ensures that patients are watched continuously without regular manual checks.
Enhanced Patient Engagement and Satisfaction
Many of the contemporary HMS solutions include patient portals through which patients get access to their records, test results, or treatment plans. This aspect of transparency breeds active engagement in self-management of health, increased satisfaction rates, and trust in the services offered by the hospital. To further enhance this engagement, healthcare facilities are increasingly using digital tools to simplify how patient contact details are captured and stored. Solutions like Uniqode: digital business card allow hospitals to instantly collect and sync patient or visitor contact info directly into the system—ideal for walk-ins, health camps, or outreach events. Patients are also able to come in through these portals to book appointments, request refills on prescriptions, and to direct communication with providers in regard to care services.
Operational Efficiency and Workflow Optimization
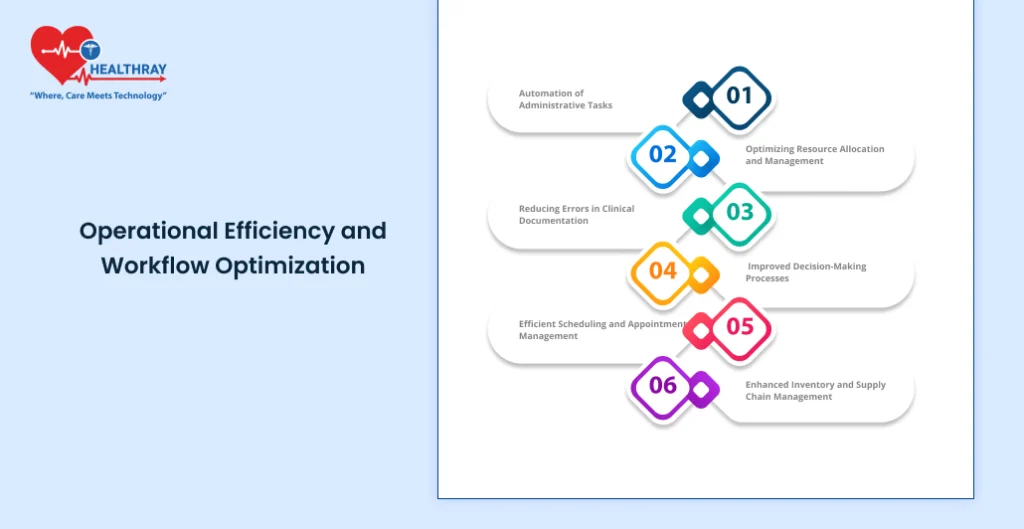
Modern HMS not only enhances the scene of patient care but also the very process of functioning of any hospital. Integrating the processes and optimizing the management of resources, HMS helps the healthcare facility to deliver well in the functions. Here is how HMS improves operational efficiency in all aspects of hospital management:
Automation of Administrative Tasks
Administrative work is a lengthy process in health care, where patients have to go through lots of redundant tasks of registration, billing, discharge processing, insurance claims, and others. HMS helps eliminate lots of those redundant processes so that free time will be available for administrative staff and eventually reduce the risk factor of human error. It will increase the processing speed and ensure proper recording of all kinds of important information from admission till discharge so that it ensures a smoother experience with the patient.
Optimizing Resource Allocation and Management
Hospital multispecialty sites that admit a large number of patients have strict resource management. An HMS can help monitor the distribution of the occupation of rooms and other equipment such as medical tools. For instance, an HMS may offer immediate information on the number of occupied beds available, hence better patient admission management. In addition, with respect to tracking usage and managing medical equipment, HMS keeps the scarcity of resources at bay; healthcare professionals possess what they require, when it is required.
Reducing Errors in Clinical Documentation
Proper documentation is an essential part of health care. Errors in a patient’s treatment, medication, and other care can be due to poor documentation. The electronic format of documentation via HMS reduces the incidences of errors due to documentation on paper or by manual updating of records. The use of HMS will ensure that patient information is in a digital format, thereby keeping all the relevant and accurate information regarding the patients with the healthcare service providers at their fingertips. Documentation on accuracy facilitates quality patient care with the aid of minimizing the possibility of errors that may cause complications or legal liabilities.
Improved Decision-Making Processes
Hospital decisions need to be fast, correct, and data-driven. HMS provides hospital administrators with rich analytics and reporting, using which they could see into a hospital’s performance, patient trends, and the operational bottlenecks. Data-driven insights from HMS support executive decisions in hospitals as they improve efficiency – whether adjusting staff levels or optimizing patient flow, the data from HMS powers choices that improve overall performance.
Efficient Scheduling and Appointment Management
In large health facilities, managing doctor, staff, and patient schedules is quite challenging. HMS has all its automated scheduling tools that can accommodate appointments with staff shift and allocated medical rooms and equipment. This automation erases conflicts and reduces patient waiting times since their appointments are spread evenly, and resources are well utilized. The patients wait less while the doctors or staff have scheduled and organized lives, resulting in less burnout and more job satisfaction.
Enhanced Inventory and Supply Chain Management
Hospitals rely on the assumption that supplies of medicinal supplies, drugs, and other equipment will be continuously available. An HMS thus tracks the inventory levels and alerts the management to the running lowness or near expiration of the supplies. Such pre-emptive inventory management will prevent hospital stockouts, waste the former, and ensure the maintenance of adequate stocks that will keep patient care without interruption.
Data Security and Compliance
One of the top concerns of hospitals and other healthcare providers today is data security in the modern, high-tech healthcare environment. Deterrents like confidentiality and trust towards this sensitive data are essential not only to keep the consumer’s trust but also to meet the regulatory standards. HMS of the modern era contain sophisticated security features that protect the data and ensure compliance with health care regulations. Here’s how these systems contribute to data security and compliance in the health care sector:
Protecting Patient Data with Encryption
Data encryption is the most primary way of protection for digital information. Current HMS solutions employ encryption for the protection of patient data when it is being stored and sent. This way, access to and interpretation of the data will be strictly within the confines of people who are authorized to do so, hence, with no possibilities of unapproved access or data leakage. It becomes impossible to intercept sensitive information including health histories, diagnoses, or treatment plans.
Access Control and User Authentication
The access control of hospital management systems is strict to allow only authorized persons to read or update specific data. HMS limits access to certain data based on the role of the user in the hospital using multi-factor authentication and role-based access control. For example, some doctors and specialists may have full access to patient records while administrative staff may have rights only to access billing information. Such structured access definitely reduces the risk of data breaches and improper internal use.
Audit Trails and Activity Logs
For accountability purposes, HMS features an audit trail, that captures each and every interaction with the system. Accordingly, an audit log will capture access to specific data, changes in the system, and at exactly what time these interactions occurred. In cases of a breach or unauthorized access to some data, administrators will be able to track logs to identify some security gaps and rectify them. Further, this feature increases security but it also demonstrates compliance with regulations, such as requiring transparency over data accountability.
Compliance with Healthcare Regulations
Hospitals are driven by vast regulatory requirements, from HIPAA in the United States to GDPR in Europe and regional regulations. The HMS of the present era is designed to comply with such regulations by implementing data protection policies, user access controls, and secure methods of storing data. Compliance prevents such penalties or court charges while building patient confidence through adherence to the protection of information they provide.
Regular Security Updates and Patch Management
Healthcare management systems should always find themselves on the frontline of latest protections against risks of cyber threats. Regular updates and patches from HMS providers help to eliminate the risk of potential breaches and improve the measure of security built into the system. In this light, a reduced risk of a cyber-attack would be able to step up the data protection built into the hospitals to standards.
Data Backup and Disaster Recovery
After a system failure due to cyber attack or natural disaster, the most important requirement for reliability is in backup and recovery of data. Most HMS solutions include some kind of data backup as part of the system where such records are safely stored in some secure location other than a location of the organization. This ensures speedy restoration in case of an emergency, saving the hospitals from loss of data and minimizing the period for readmittance of patients to healthcare. Disaster recovery measures are a part of making sure data integrity is maintained as well as compliance.
Challenges in Implementation and Solutions
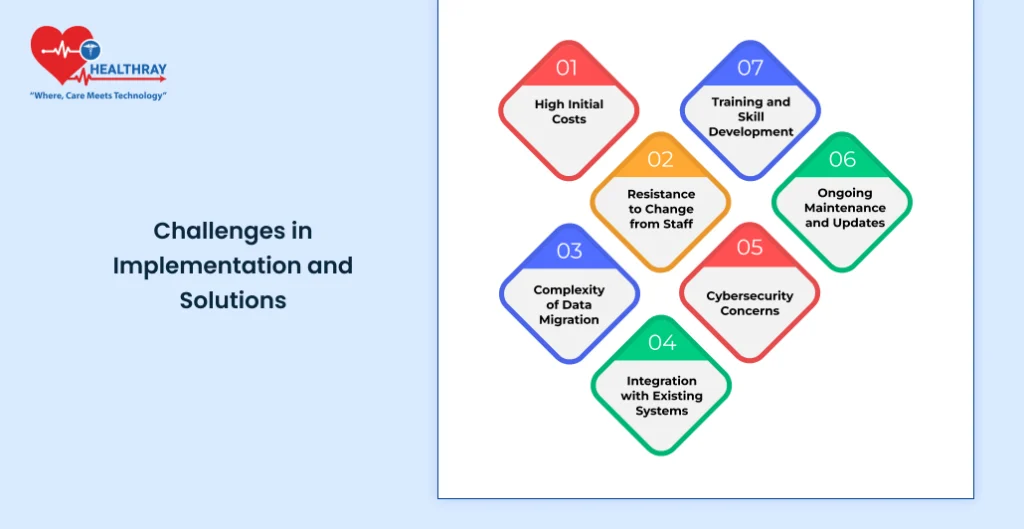
While the previous HMS systems had certain benefits, the modern HMS systems have their own sets of problems concerning implementation. From technological to resistance from the staffers, hospitals have to pass through these hurdles just to be able to implement and integrate these systems into their respective workflow. Here are some common challenges in implementing an HMS coupled with practical solutions:
High Initial Costs
A robust HMS would become a component of every comprehensive HealthCare Management Systems, that necessitates upfront investment in hardware, software, and infrastructure enhancements. Such high costs often put a pinch on small healthcare facilities. Nevertheless, the long-term benefits from reduced paperwork, enhanced efficiency in operational values, and right allocation of resources outweigh the long-term upfront cost. The installation can be phased, or even financed for easy transition into the system.
Resistance to Change from Staff
Change is not easy, especially in high-stakes environments like healthcare. Some healthcare providers and staff may be bound to fear disruption in their job because of the new HealthCare Management Systems, or just because they are unfamiliar, or because of the fear of workload increase. Involving staff in the initial stage of decision-making process, providing clear communication regarding the benefit of the system, and offering comprehensive training programs and continuous support can lessen the shock of change and build staff’s confidence in using the HMS.
Complexity of Data Migration
A digital marketing agency specializing in healthcare can assist with extensive data migration, including patient records, billing information, and administrative data, seamlessly transitioning from paper-based or outdated digital systems into a new HealthCare Management System. This process should be done very carefully so that the loss or error is not caused by any data. For that purpose, hospitals will require experienced IT professionals who have experience with health management systems along with an HMS provider that supports data migration. Finally, they should also validate the data thoroughly post-migration to get accurate results.
Integration with Existing Systems
Almost all hospitals already have specific systems for managing radiology, laboratories, and pharmacies. Bringing in a new HealthCare Management System would be difficult to interface with these legacy systems. This would especially be an issue if the systems were from different providers or using older technology. It will be easier to communicate between the different systems if one chooses an HMS that supports openness standards and interoperability. Vendors who understand their integration issues should also be easy to find.
Cybersecurity Concerns
For example, developing an HMS has introduced cybersecurity threats to the company. The HMS deployment shares risks to patient data information, where it makes sure that any legislation from health care will be followed. Cyber security is one of the specific security measures this includes encryption, updated security updates, and limited access controls. Staff also is educated in the cyber security best practices that prevent the risk of human errors during breaches.
Ongoing Maintenance and Updates
This is not a one-time process; the HMS needs to be maintained on a regular basis, updated, and given adequate technical support in order to be used effectively. These needs are very demanding, especially for hospitals that do not have dedicated IT staff. A good partnership that ensures continued support and maintenance plans might be necessary with a stable HMS provider. The system security, compliance with regulations, and current features keeping pace with the changing demands of healthcare are all serviced through these regular updates.
Training and Skill Development
Since a new HealthCare Management System should be effectively adopted by the health staff, they need to be trained. It can be very time-consuming especially for large hospitals. There should be role-specific training programs presented to every department along with on-the-job training apart from continuous education focusing on new features and functionality.
Case Studies
Real-life examples of how hospitals implement modern HMS can be regarded as a good means of viewing the practical benefits of these systems. Outcomes in various health care settings reflect how HMS solutions impact patient care, operational efficiency, and data security. Some case studies are included here as illustrations of successes and learnings arising from the adoption of modern HMS technology:
Multispecialty Hospital in a High-Density Urban Area
Association with troubles in the multispecialty city center, which is densely populated, management of the patients was done in this hospital. This hospital does not manage data availability, staff coordination, and patient flow appropriately. Advanced HMS with capabilities of EHR integration, automated scheduling, and IoT-based patient monitoring were deployed in this hospital.
Outcome: In six months, the hospital reported a 20% reduction in wait times by patients and 30% increase in administrative efficiency. The EHR had already proven to stream-line doctors’ access to the entire patient history in no time, reducing treatment delay. With automated scheduling, appointment conflicts were minimal, leading to enhanced patient satisfaction. The IoT feature gave real-time monitoring of patient vital signs, thereby reducing constant manual checks and freeing up staff for critical care.
Rural Community Hospital Adopting Telemedicine
The specialty care access was minimal at this rural hospital, hence the need to find a solution to deliver timely consultations to patients without much traveling. An HMS was implemented at the rural hospital, thus allowing virtual consults with distant specialists.
Outcome: Specialist consultation rates rose by 40%. Telemedicine promoted access to quality care to remote patients without having to deal with travel-related difficulties. Patient satisfaction scores went up because they appreciated the convenience, and the hospital reported the improvement in treatment adherence following the ease of scheduling and following through with follow-up consultations. This case serves to explain how telemedicine in an HMS can bridge the so-called geographical gaps that make care more accessible.
Large Hospital Network Focused on Data Security and Compliance
A large hospital network operates in different branches at numerous locations. Under these, very large challenges emerged in terms of data security, regulatory compliance, and system integration at the level of branches. A cloud HMS has been deployed by the organization using encryption and access control and regular audit trails to preserve data integrity and ensure requirements like HIPAA are complied with.
Outcome: The network shows great results in securing the data since no data breaches were reported during the implementation period. The compliance features of the system ensured that every one of the branches was working under the uniformity of the regulatory standard so that the audit handling and penalty evasion could easily be handled. Secure accessibility to the patient data of staff stationed at different locations led to coordination improvements as well, and smooth patient care streamlines smoothly across the hospital network. This vivid example drives home the point that a HMS must be centrally located and compliant to offer security, especially with data, across various facilities.
Specialty Hospital Improving Resource Management and Cost Efficiency
A specialist hospital dealing with heart diseases faced huge resource utilization issues. There was a frequent shortage of equipment, and other patient procedures were delayed due to improper scheduling. The introduction of HMS, which tracks the usage of equipment and manages schedules for operating rooms and beds, optimized resources within the specialist hospital.
Outcome: The hospital increased resource utilization by 25% and reduced operational costs by 15% in the first year. In the critical care unit, through monitoring and managing the usage of critical equipment, the hospital reduced downtimes and improved patient throughput. The staff members saw a significant reduction in the possibility of double-booking by the automated scheduling feature, hence smoother operations and more satisfied patients.
Mid-Sized Hospital Enhancing Patient Engagement and Satisfaction
A mid-sized hospital aimed to increase patient engagement by making health information more transparent and accessible. For that reason, the organization implemented HMS that includes a patient portal where patients can access their health record and test results and can provide them with an opportunity to communicate with their healthcare providers.
Outcome: There were significant increases in patient engagement through increasing portal logins by 35% and improving the quality of feedback. Patients were happy about gaining access to their records and communicating directly with providers, which helped build trust and satisfaction. Administrate inquiries also declined as most patients could clear their information themselves.
Future Trends in Hospital Management Systems

Advanced HMS: Healthcare is changing day by day, and so is a hospital management system. These systems more and more are adapting technologies that improve efficiency, care, and their rate of adaptation in a digitally transformed health environment. Some emerging trends that will shape the future of HMS over the next few years:
Greater Use of Artificial Intelligence and Predictive Analytics
AI and predictive analytics will play a larger role in HMS, transforming the way hospitals interact with patient data, resources, and treatment plans. AI can analyze large datasets for patterns, predict the patient’s needs, or suggest a perfect measure in preventing a condition. For example, it can predict patient admission so that it is easy for hospitals to make accurate allocation of resources. This trend will not only help optimize the running of the hospital but also deliver more proactive, personalized care to patients.
Expansion of IoT-Enabled Devices
IoT will keep on growing, with further devices linking into the systems of hospitals. IoT technology will enable the remote patient monitoring capabilities, which in turn track all real-time vital signs, medication adherence, and post-operative recovery. The connectivity would ensure that the positive outcomes for patients, especially high-risk and those remote, are achieved since healthcare providers could monitor their condition at all times. This is where the trend comes in, and hospitals can improve patient care within the facility and even at the comfort of the patients’ homes.
Increased Adoption of Blockchain for Data Security
Blockchain technology is one of the best approaches currently used in managing health care data safely. This decentralized, tamper-proof ledger can enable hospitals to maintain integrity and confidentiality for patient records. As such, blockchain technology will ease data sharing between hospitals and healthcare providers while ensuring security and patient consent. Its importance in health care data security will be increased as data privacy issues continue to rise.
Emphasis on Cloud-Based Systems and Interoperability
Cloud-based HMS would remain an all-important trend, particularly because of the scalability and cost-effectiveness in pursuit by hospitals. Cloud systems allow health care providers to view patient data from anywhere, especially useful for multispecialty hospitals and multiple branches. Interoperability-the ability of systems to work in collaboration with each other-would be major also. Thus, future solutions in HMS would aim at greater integration, allowing seamless interaction between the different departments as well as external healthcare entities leading to better coordination and interoperability in care.
Incorporation of Virtual and Augmented Reality for Staff Training
Virtual and augmented reality technologies are increasingly being used as effective tools in the training of health care professionals. These technologies will provide an immersive and hands-on learning environment, which is greatly useful for surgical training and simulating emergency response. Future HMS can include modules of VR and AR to train staff. This will enhance the preparedness and skill development of the staff. This trend aims to enhance quality care not only by appropriately trained healthcare workers but also through their confidence in delivering services.
Focus on Patient-Generated Health Data
Patient engagement with health is now generating data through wearable devices, health apps, and online portals. Patients will now be able to generate health data that can potentially become part of future HMS. Healthcare providers will, therefore, be better apprised of a lifestyle and the health metrics of the patient. Such data will support both preventative care and treatment customization. Patients can take an active role in their management of health at the same time as doctors gain such valuable insights outside traditional clinical settings.
Growth of Personalized and Precision Medicine
Improvement in genetic and data analysis is leading to an individually tailored approach to therapy. Future HMS would, therefore, integrate genomic data where hospitals offer precision medicine to tailor to individual patients based on their genetic profiles. Tailoring therapies to specific genetic and lifestyle factors of each patient might improve the outcomes of chronic diseases, cancer, and other complex conditions.
Enhanced Telehealth and Remote Care Capabilities
The use of telehealth and home-based care shall be on an ascent because patients are seeking easily accessible healthcare. Future HMS shall continue in the expansion of telehealth options by even more favorably reaching patients and making health care professionals accessible out-of-office. Remote diagnostics, follow-ups, and chronic disease management will also be supported especially to patients who are living far out or based in underdeveloped countries.
Conclusion
The modern HMS has been indispensable in reaching toward a fully digital healthcare environment. Hospital Management System reshapes not only administrative efficiency and patient care but also moves hospitals toward a tomorrow where technology combines with health appropriately to make the difference. By embedding the advanced features of artificial intelligence, IoT integration, telemedicine, and data security measures, hospitals are able to meet the demands of today’s patients and improve the outcome for overall operations.
For health care administrators, IT professionals, and hospital executives, adoption of an HMS is no longer an option; it has become a strategic imperative in pursuit of being competitive, compliant, and capable in this fast-evolving landscape. There are numerous benefits that a good HMS offers beyond mere cost savings: enhancing patient engagement to data security and the right use of resources. These are systems that will serve as the basis for long-term growth and adaptability with better delivery of healthcare regardless of the size or level of specialization of the hospital.