Introduction
How can a hospital management system deliver inordinate improvement in patient care? Efficiency and accuracy are primarily essential to hospitals or doctors who treat increasing numbers of patients. An HMS, implemented properly, can deal with everything from scheduling to medical record handling, thereby decreasing errors and improving treatment techniques. Thus, this article proceeds to describe how HMS optimizes hospital workflows, which in return benefits patient care and satisfaction directly. This article will cover immediate benefits as well as how the system supports long-term improvements, including telemedicine and data security. Let’s discuss why HMS is important for contemporary healthcare settings in depth.
What is a Hospital Management System (HMS)?
A Hospital Management System is an all-inclusive digital solution, as it handles not only the administrative but also the clinical aspects of a hospital. Patient registration is done to electronic health records or billing; that is, the HMS ensures a smooth performance of all activities within a hospital. It gives zero room for human-made errors and manual procedures, so there is increased time to care for patients.
HMS connects the different departments together, ensuring all data, from patient history to lab results, can be easily accessed in real-time. Improved communication and record-keeping help doctors make more informed decisions and deliver personalized treatment to patients.
Enhancing Patient Care with HMS
One of the most significant ways HMS improves patient care is by centralizing patient records. A single system that holds all patient data allows doctors and healthcare professionals to access complete medical histories instantly. When critical decisions need to be made quickly, having a patient’s history, test results, and medications in one place can make a difference in the quality and speed of care. It minimizes diagnostic errors and ensures better coordination between departments.
Another notable advantage is how appointments are efficiently set up. These HMS systems preset schedulers for the patient to see the doctor based on availability and prioritization. This decreases the length of time a patient is required to stand in line while helping optimize the resources of the hospital. For instance, in a very active emergency room, a delay of care in high-priority cases is not needed because the doctors are able to see the patients without the constraints of the system, thus decreasing resource allocation strain.
The system also improves the adherence to the therapy by logging the prescriptions, their quantities, dosage, and possible combination side effects. In turn, when patients have polypharmacy needs due to many ailments, the system reduces potential errors with automation of the processes.
How HMS Support Telemedicine and Remote Care?
Outpatient care has grown since the time of the Corona Virus pandemic, so has the use of technology, which has enabled diagnosis and treatment at a distance with great ease. Putting medication prescriptions on these systems is a plus. They make out of the box solutions to facilitate telemedicine by placing remote consultation features. Patients do not need to step on the hospital premises; they just book and attend virtual appointments through the prescription system.
With the introduction of HMS, telemedicine also widens healthcare access because practitioners are able to see patients through devices with the patient in their home. The devices range from normal mobile to sophisticated wearables that monitor vitals continuously. This makes it possible for doctors to manage patients proactively and initiate treatment, even when the patient is not physically present in the care facility.
Patients with chronic conditions benefit greatly from remote supervision. It ensures consistent monitoring in situations where it is highly needed.
Strengthening Operational Effectiveness to Enhance Patient Satisfaction
The entire experience that a patient receives is directly proportional to how well care givers perform in the hospital and how HMS performs. A good example is the automation of billing and other information such as the control of the inventory and reporting. It relieves personnel a great part of their workload. Consequently, the concentration of hospital staff shifts from dealing with much paperwork to concentrating on the care of patients.
For instance, patients receive bills with itemized receipts without tampering so the facilities billing becomes easier to understand. Effective provision of resources like the distribution of hospital beds and medical supplies leads to better theatres utilization. Patients receive treatment with less waiting time.
Moreover, the HMS is also used to control inventories of medical supplies, drugs, and medical equipment. Shortages are also prevented by alerting the hospitals when the supply is low. This is relevant during emergencies, where patients need immediate treatment. Such readiness is necessary for the safety of patients and the continuity of their care.
Data Security
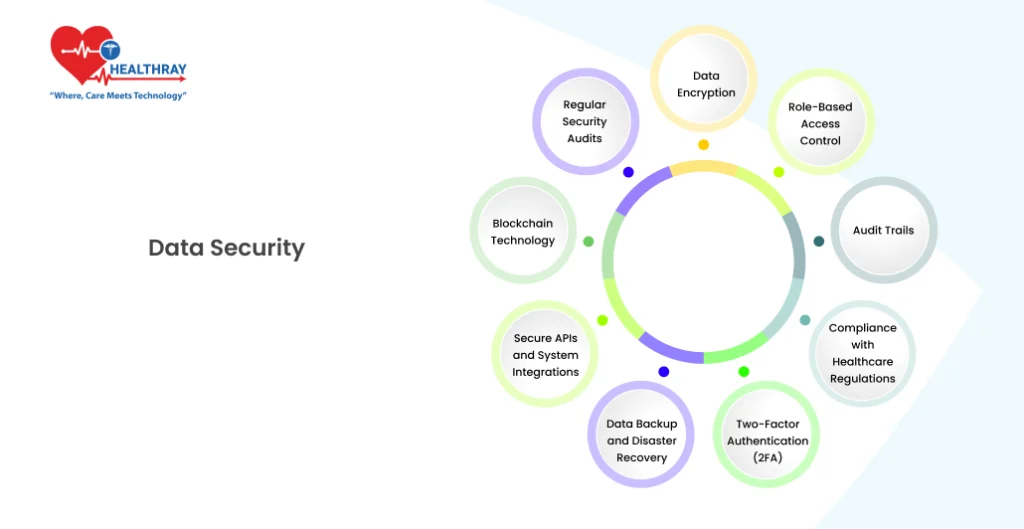
Safety of data and regulatory conformance are paramount for hospitals as they deal with large amounts of patient data that is often sensitive. Hence, data security must be considered when designing Hospital Management System (HMS).
If adequate protection does not exist with unintended access or data breaches, it can result in significant problem from legal and financial point of views. The following are the main approaches HMS uses to ensure data security and meets international healthcare standards.
Data Encryption
Encryption mechanisms are used in cases of HMS to safeguard data on the servers storing databases as well as during data transfer between. Thus, although an individual may succeed in circumventing security, neither can they comprehend the data unless the appropriate decryption key can be found. Advanced cryptographic techniques, such as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard), are used to ensure maximum security.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
HMS platforms provide role-based access control, ensuring that people have access to specific information only as part of their role in the HHS health organization. For instance, a nurse could be able to extract only components of the patient care record while the billing staff can extract components of the financial record but not the medical record. This approach prevents that personal data from being accessed without authorization, reducing the potential for an internal data leak.
Audit Trails
HMS systems provide complete audit logs which record all actions occurring within the system. No matter whether it is the doctor who makes a patient record entry or a bill is billed by administrative staff, recording dates all changes is maintained. This facilitates audit of who accessed or edited data, which in turn assists in accountability and allows for rapid review of any data discrepancies.
Compliance with Healthcare Regulations
Complying with regulations such as HIPAA in the US and GDPR in Europe is a necessary condition for Hospitals to safeguard patient privacy. HMS platforms are designed to meet these regulatory requirements.
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
In order to increase security, many Hospital Management Systems (HMS) are equipped with 2-factor authentication. This added security layer above a standard username and password now involves a One Time Password (OTP) being generated on the user’s device.
Data Backup and Disaster Recovery
Information can be irretrievable through hardware failures, cyber attacks and/or natural disasters. HMS systems provide assurance that routine patient data backups are stored securely, often in clouds, so that restoration can be achieved easily in the event of a system crash. These backup mechanisms are built to be robust and enable emergency recovery, so that hospital operations can remain unchanged.
Secure APIs and System Integrations
Hospitals are frequently required to link their HMS with external systems (i.e., laboratory software, pharmacy management systems, third-party healthcare applications), etc. HMS platforms rely on secure Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) which adhere to strict security practices to protect clean data exchange between disparate systems while maintaining integrity of the data.
Blockchain Technology
Although still under development, the technology of blockchain is being tested as a means of safeguarding patients’ records. Using tamper proof ledger of patient data, blockchain can help guarantee the immutability of data and facilitate secure data sharing among healthcare professionals.
Regular Security Audits
Regular security audits are an essential part of maintaining the security of an HMS in a technological changing world. These audits help hospitals identify potential vulnerabilities and address them proactively before they can be exploited, which is increasingly important as cyber threats become more advanced.
Challenges and Considerations in Implementing HMS
Despite the benefits of a Hospital Management System (HMS), stakeholders are often frustrated with implementing HMS. A typical problem is staff resistance to change, particularly at facilities where paper-based workflows have long dominated the scene. Successful uptake depends largely on providing deep training and using robust change management techniques. By demonstrating to staff how an HMS can reduce work and enhance the delivery of patient care, it is possible to increase acceptance substantially.
An even greater challenge is the cost of the investment in an HMS. For smaller hospitals, the upfront costs can seem daunting. Nevertheless, the benefits on a long-term level (e.g., reduced operational expenses, and increased patient benefits) justify the cost. Further, hospitals must also be prepared for potential data transfer problems during the process of transferring the existing records to the new system.
Integration with existing systems, such as pharmacy or laboratory management systems, is also not straightforward. Selecting an HMS which can be flexible and subsequently integrate well should facilitate an easier transition.
In Summary
Adopting a Hospital Management System can lead to significant improvements in patient care by boosting efficiency and ensuring that all departments have timely and accurate access to medical information. Healthcare providers benefit from reliable data, allowing them to make quicker and more informed decisions. Clinician satisfaction, patient experience, and reduced patient wait time are all benefits from this change. In the end, a properly established Hospital Management System not only increases the productivity of both patients and the medical personnel through optimize workflows.patients and healthcare providers alike.




