Patient management is not an easy task in a hospital setting. Every step taken, right from admission to discharge, requires precision and care. Inpatient departments or IPDs play the lead role in timely delivery of care with judicious use of resources.
The challenges most frequently faced by healthcare administrators, hospital management professionals, and medical practitioners relate to unorganized patient data, inefficient bed allocation, or cumbersome billing processes. The right set of features in IPD can convert such challenges into opportunities and streamline operations to attain better outcomes.
This posting discusses the major components of a modern IPD software system that should be included in order to support a hospital’s provision of quality care with effective utilization of resources. Implementation strategies, along with the adoption barriers and their solutions, are also discussed.
Importance of IPD In Hospital
Comprehensive Care
- From the bed management to IPD billing services, it administers all tasks efficiently. Also, patients get psychological support that helps in accelerating recovery rate.
- Administers complete treatment surgeries from ward management to post-operative surgical care. Also, it helps in maintaining a safe environment.
Persistent Monitoring
- Through the single healthcare platform, it is much easier to know the details of patients and their exact locations.
- Assisting to inspect earlier signs that might be a hurdle in clinical surgeries, centralized information helpful for making practical decisions.
Enhances Patient Safety
- Applies a varied number of safety measures that prevents medical information from cyber attacks, reducing medical expenses.
- It encompasses data encryption, access control, compliance with medical guidelines like HIPAA, European Commission, and others.
Key Features of Inpatient Management Software
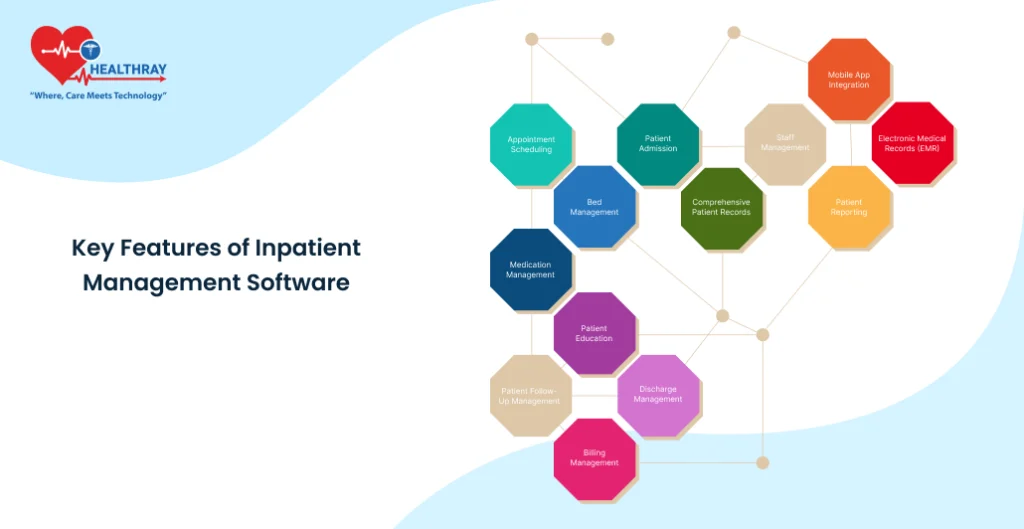
Modern inpatient management systems have now become the backbone of efficient hospital operations. Key features that must be there with every robust IPD for optimum patient care and management are as follows:
Appointment Scheduling
Efficient scheduling ensures that patients are seen at the right time and without overloading staff or resources. Automated systems remind patients and execute appointment bookings at a much faster rate, saving time and minimizing the number of no-shows.
Bed Management
Real-time bed tracking and allocation help optimize bed occupancy rates, thus ensuring that no time is lost in finding available beds during crucial admissions and discharges.
Patient Admission
A well-designed IPD system simplifies the process of admission by reducing paperwork, thereby speeding up the onboarding process for patients. The result is an improved patient experience and reduced administrative burden.
Comprehensive Patient Records
This means that with centralized patient records, medical history, lab analysis results, and ongoing treatment records are easily referred to by healthcare professionals to ensure that every decision is well-considered and accurate.
Staff Management
Efficient staff scheduling thus allows for better task allocation and optimum staff-to-patient ratios. This helps manage the workload of hospitals and in turn provides better care for the patients.
Mobile App Integration
Mobile applications can be used to access patient data by doctors and staff while on the go for quick decisions, hence assuring better care even when off-site.
Electronic Medical Records (EMR)
Seamless integration of EMR allows continuous updating of patient information accurately and easily shared along various departments for better coordination of care.
Patient Reporting
Patient reports prepared in detail describe the conditions, treatments, and progress. These are highly important both for medical teams and patients.
Medication Management
The monitoring of prescribed medicines and administration schedules helps reduce errors in the treatment process and assures patients receive the right treatments at the right times.
Patient Education
The condition-specific education provided to the patients helps them understand the care plans better and builds trusting relationships between the patients and providers.
Discharge Management
Automation of discharge processes reduces delays that block the admission of new patients, hence improving patient satisfaction.
Billing Management
Accurate billing systems are characterized by transparency in that treatments and services provided will generate an itemized bill.
Patient Follow-Up Management
Follow-up scheduling during discharge planning ensures continuity of care and better recovery outcomes for patients. Tools like The QR code generator can help streamline this process by allowing hospitals to share appointment reminders, teleconsultation links, or digital instructions via scannable codes offering patients easier access to essential post-discharge care information.
Implementation Strategies for IPD Features

Advanced features in an inpatient department require prudent introduction and follow-through. Here are practical strategies that will assist the health administrator and the management team in implementing such features:
Assess Current Systems and Needs
Study the existing system at the hospital first, and then identify lacunas before introducing new features. This will ensure your understanding of specific requirements at the hospital when you choose features in line with goals for operations.
Choose Scalable Solutions
Choose scalable software systems in your hospital for future needs that may arise as a result of an increase in the volume of patients or the addition of other functionalities that may be needed.
Engage Stakeholders
The process for selection and implementation should involve doctors, nurses, as well as administrative staff. These parties will contribute to the assurance that the system will meet practical needs while building support for the system from all levels of the organization.
Prioritize Integration with Existing Systems
New functionalities at IPD must be integrated successfully with current hospital functionalities such as EMR, lab management, and billing services. Compatibility reduces disruptions, thus allowing for a smooth workflow.
Invest in training for your people
Even the most elegant system is only as great as the people who work to utilize it. Organize more practical training sessions so they become familiar with new facilities, like nonpharmacological pain management devices offered by Sensonica. Include troubleshooting methods whereby teams can handle minor problems independent of the help needed in their departments.
Implement Gradually
Roll out features in phases so as not to disrupt operations. For example, do appointment scheduling and bed management first before integration with patient records and billing. This allows time for adjustments and feedback.
Monitor and Evaluate Performance
Track KPIs on patient satisfaction, staff efficiency, and resource utilization. Regular assessments will provide focus on adjustments and ensure delivery of the expected benefits of the system.
Ensure Compliance with Regulations
Adherence to health-related regulations in terms of data privacy, among others, is paramount. Co-operate with your software provider for compliance and addition of features adding extra layers of security.
Provide Continuous Support
Establish a support system for prompt resolution of technical issues. Continuous support means smooth operations and instills confidence in the users.
Collect Feedback Post-Implementation
After the deployment of features, take the feedback from staff and patients. This should be used to fine-tune the system concerning its shortcomings.
The strategic implementation of the features of IPD has ensured not only better patient management but also increased operational efficiency, thereby assuring a better experience for both patients and staff.
Challenges and Solutions in Implementing IPD Features
Integrate advanced IPD features to transform hospital operations, but doing so is usually not easy. A few of the common challenges faced by hospitals and some practical solutions to overcome them include:
Resistance to Change
Challenge:
The resistance from staff to the adoption of new systems may be because they fear complication or causing disruption to their jobs.
Solution:
- Involve employees early in the decision-making process so that they feel valued.
- Ensure clear communication about the system’s benefits.
- Provide in-depth, hands-on training that fosters confidence and competence.
High Implementation Costs
This can involve upgrading or replacing existing systems, which may be quite expensive, especially for smaller hospitals.
Solution:
- Scalable systems, and modular ones, are usually better since costs can be dispersed over time.
- Look into any government grants or health care funding programs that could defray some of the costs.
- Determine the ROI by investigating the savings that come because of efficiency improvement.
Integration Issues with Existing Systems
Challenge: New features might conflict with the currently used hospital management systems.
Solution:
- Choose systems that offer compatibility with widely used software.
- Partner with vendors offering integration services combined with ongoing support.
- Test the integrations in a controlled environment prior to the full implementation.
Data-Related Privacy and Security Issues
Challenge:
It creates a higher vulnerability to data breaches with the addition of digital features.
Solution:
- Select systems with multi-factor authentication and state-of-the-art encryption.
- Train the staff on best practices related to handling data and compliance with regulations.
- Regular auditing to ensure compliance with the privacy laws.
Staff Overload During Transition
Challenges:
The transition to a new system is time-consuming for the already work-loaded staff.
Solution:
- Make feature implementations gradual to prevent business disruptions.
- Temporarily hire additional staff or leverage external consultants for the transition period.
- Offer recognition or incentive programs for employees during the transition period.
Lack of Technical Expertise
Challenge: Smaller hospitals may lack internal IT teams to manage advanced systems.
Solution:
- Choose systems that have a friendly ‘user-oriented’ interface.
- Partner with those software providers that offer technical support on a 24-hour basis.
- Outsource IT management to specialized service providers.
Unrealistic Expectations
Challenge: The hospitals may expect results right away, hence disappointing them.
Solution:
Set realistic goals and timelines for implementation.
- Explain how the full benefits of the system will be realized over time.
- Keep the stakeholders informed about progress made and preliminary results as regularly as possible.
Downtime During Implementation
Challenge:
There may be temporary operational disruptions in the shift to a new system.
Solution:
- Schedule the implementation during periods of low activity.
- Back up all important data and systems regularly.
- Then, design a contingency process for any emergencies that might occur during the transition.
Vendor Dependence
Challenge: Overdependence on one vendor usually becomes a choke point when delays in service occur.
Solution:
Research a few vendors and then choose only one with a good record.
Negotiate clear service level agreements to guarantee timely support.
Train in-house staff to manage basic system operations.
In fact, addressing such challenges in advance would smooth the implementation process. The hospitals that overcome these challenges smoothly can exploit all the advances that the IPD features in patient care and operational efficiency.
Conclusion
The core of quality healthcare delivery rests on efficient patient management. Advanced IPD Management Software features power a teaching hospital with all the arms it needs to smoothen operations, improve patient satisfaction, and optimize resource utilization. From real-time bed management to automated billing systems, these features address the common challenges healthcare facilities face and strive to provide improved outcomes across the board.
Adoption of such technologies would imply overcoming concerns for resistance to change, integration complexities, or cost concerns. However, with a strategic approach and training of staff, hospitals could very well overcome such challenges by their gradual implementation and continuous evaluation.
From healthcare administrators to Hospital Management System professionals and medical practitioners, investment in advanced IPD features is not just about smoothing the processes but is also about ensuring timely, effective, and compassionate care for every patient, which ultimately maximizes the operational efficiency of the hospital.
Identify your specific needs and then go ahead seeking scalable solutions to achieve your objectives. Equipped with the right IPD system, your hospital can set new standards in patient care and management.




