It simplifies access to data, increases collaboration among teams, and in the process leads to better health outcomes for patients. However, for a single, straightforward implementation, the hospital will have to deal with a series of actions and decisions that affect not only the medical staff, but also all administrative staff.
EMR implementation isn’t simply about installing new software. This is a question of change in the ways hospitals operate and in training all members of staff in new protocols. To do this successfully, hospitals need to be properly prepared, communicate well with their staff (and make sure this is reviewed regularly) and have an easy to tap into infrastructure to manage the transition and ensure its continued use.
In this guide, we’ll explore the best practices for implementing EMR System that can help hospitals and multispecialty practices avoid common pitfalls. We’ll cover each essential stage, from assessing readiness to training staff and setting up a sustainable support structure. Plus, we’ll touch on why having a partner like Healthray.com can make this transition smoother by offering the tools and resources hospitals need to manage and optimize their workflows effectively.
Assessing Readiness and Defining Goals

None, but it is important for hospitals to start thinking about how their current condition and what they want an EMR to do now, before stepping into an EMR implementation cycle. This step is not only a question of understanding technology, but also a question of what level of readiness the entire hospital team should have in order to embrace this change and realize the change. Here’s a structured approach for this initial phase:
1. 1 Understand Organizational Needs and Workflow
All hospitals have their own workflows and there are ways of working that need to be taken into account when installing EMR software. Begin by identifying the specific needs of your organization. This entails evaluating patient data management, documenting the process involved in each patient care encounter, and identifying existing impediments.
Document Key Processes: Characterize the key workflow, from registration to discharge, and briefly describe each process. This may suggest regions of the EMR in which value can be immediately delivered, e.g., by shortening the period of document completion, or when data is obtained more seamlessly between departments.
Identify Bottlenecks: Notice any existing bottlenecks to staff workflow or on the patient side. But these are examples where an EMR system could have added real value for instance by reducing lag or by facilitating better interaction.
1. 2 Set Clear Goals and Expectations
Now, if you have an idea of what you need, then it is time to become, as specific as it can be, achievable and (sequentially) measured, in order to achieve your EMR implementation goals. If goals are not explicitly in place such undertakings can easily go off topic or the various work groups can have different expectations.
Define Success Metrics: Think about what success looks like for your hospital. Performance measures might include increased patient throughput as a result of efficiency gained for administration or increased accuracy of performing patient data manipulation.
Establish a Timeline: A realistic time schedule is not only to avoid project burnout but also to control the schedule. It is worth to take into account the fact of potential delays and accumulate spare time for some of the processes that might require rework or adjustments in the future.
Outline a Budget: Budgeting isn’t just about the software. It shall have training, data transfer, hardware and post-implementation support that makes the shift as easy as possible.
1. 3 Form a Steering Committee
Supportive of the purpose of a structured team to lead the National EMR rollout is another key factor that needs to be addressed. The steering group of this work should represent departmental representation over the course of hospital sections and a structured, multidisciplinary, approach that is likely to be able to accommodate a range of needs/desires and perspectives.
Select Key Stakeholders: The participation of members of Information Technology, administration, medical workers (physicians and nurses). This ensures each department’s workflow needs are considered.
Assign a Project Lead: As a matter of fact, give us a person with good organisational communication skills to assist in overseeing the whole process, to keep track of the milestones and to achieve the hospitals objective.
Hold Regular Meetings: Frequent sessions with the committee allow consistent agreement and opportunity to discuss problems, suggested solutions and other relevant topics, and so on.
1. 4 Consider Healthray.com for Workflow Preparation and Support
Healthray. com can be a valuable partner during this phase. Their technology and materials are anticipated to allow healthcare facilities to evaluate team preparedness, redesign how work is organized, and prepare the needed infrastructure to successfully complete an EMR rollout. Their knowledge can, for example, offer a more efficiently structured route to the solution of highly complex problem areas, can provide the type of information that leads to a reduction in the learning curve for hospital personnel, and can assist in the adoption of EMR.
With a defined understanding of today’s needs, a defined set of goals, and an engaged interdisciplinary team, hospitals can begin to lay the foundation for successful and effective EMR implementation. This preparation phase has immense merit in that it puts the organisation back together on a to joint view, therefore, will lead to much less resistance to change for everyone.
Building an Implementation Roadmap
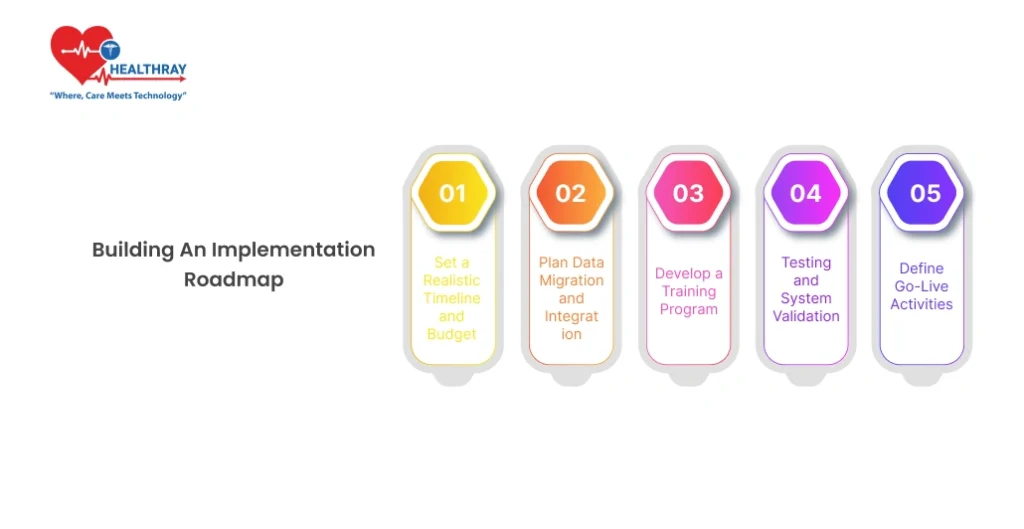
2. 1 Set a Realistic Timeline and Budget
As an initial step in the roadmap, an achievable EMR implementation period needs to be defined. This ensures that each stage is correctly prioritized and introduces the possibility to adapt as necessary, without compromising the project.
Timeline Stages: Divide the timeline into stages, such as data migration, staff training, system testing, and go-live preparation. Each phase should be accompanied by a beginning date and an end date to ensure that the schedule is maintained by the team.
Factor in Contingencies: Software projects often encounter unforeseen challenges. Give extra time in your timeline to “stuff” potential problems, e.g., unexpected data migration time or training time lost.
Set a Comprehensive Budget: Cost all aspects, i.e., software acquisition and sum of data transfer, hardware upgrade and employees acquisition at a project lifetime. Provision for latent need is equally wise, and provision for improbable need should not be disregarded.
2. 2 Plan Data Migration and Integration
Data migration is one of the most difficult, if not the most difficult, process involved in EMR implementation. Sustained data transfer between heritage systems and the new EMR has a central role in the ability to maintain continuity in the delivery of patient care.
- Assess Current Data Quality: Start by auditing existing patient records. Because errors/out of date information in existing data will be extrapolated into the EMR system, it is important to spend time on data quality verification to minimize time and labor further.
- Establish a Migration Plan: Explain how information is being transferred from the old system to the new one. This includes deciding whether the migration will occur all at once or in stages.
- Integration with Existing Systems: That continuous bed integration should be achieved with the other main hospital applications (e.g., billing, lab) of the EMR system. This interoperability facilitates automatic data movement between departments that in turn will help to improve efficiencies over the organizational whole.
2. 3 Develop a Training Program
Successful EMR implementation hinges on all users feeling understandable and comfortable with the new system. Training is a key part of the roadmap as it progresses the concerns of future users and creates confidence.
- Role-Specific Training: Customize training sessions for different roles. Thus, to achieve their goals, physicians will need specific assistance with reading patient notes, and administrators will focus on tasks such as booking and invoicing, etc.
- Hands-On Training: Include practical tasks whereby personnel can actually reproduce the system in daily life. By a similar method a user can gain an understanding of the system before its use on patients.
- Provide Access to Support: Provide users with access to support channels allowing them to get questions answered or issues solved as they become familiar with the new system.
2. 4 Testing and System Validation
Before launch, thoroughly test the EMR system so that it conforms to hospital specifications and works as designed. Testing is an important process to detect and avoid any design issues before finalisation.
Run Simulation Tests: Perform simulations of realistic hospital processes, ranging from registration to discharge. Testing of every function enables the team to detect and correct issues live.
2.5 Define Go-Live Activities
The go-live phase is defined by the official transition to the EMR system. This aspect of the roadmap should define specific activities, including techniques, for a smooth transition during this transition phase.
- Plan for a Phased or Full Rollout: Decide whether the EMR system will launch in stages or all at once. A phased rollout can ease the transition by allowing time to address any issues that arise.
- Lower Patient Volume temporarily: Consider using the go live period to provide a temporary solution of reducing volume. This approach will give personnel more time to negotiate the new system without added strain from a regular schedule.
This gives a clear roadmap, so the hospitals can proceed from planning to the go-live event with full confidence. Such structured approach will improve the chances of having a smooth roll-out process, and also get the hospital prepared for a long-term successful transition towards digital records.
Go-Live and Post-Implementation Support

The go-live phase is the critical point when the EMR system is introduced into daily hospital operations. This phase demands proper planning and strategic execution to minimize disruptions, support staff, and ensure a smooth transition. The post-implementation support is equally important to address ongoing challenges, maintain system performance, and continue optimizing workflows. Here’s how to approach go-live and post-implementation for lasting success.
3.1 Select a Go-Live Strategy
The EMR system can be implemented entirely at one time, or phased in. Both methods have their benefits, and which approach would be more suitable for the hospital depends on its resources, staff readiness, and the complexity of the EMR system.
Big Bang Approach. Hospital implements EMR to all areas simultaneously on a single day. Though effective, this approach is sometimes inhuman because it creates an enormous overload on staff. It needs the following preparation from the pre-launch training phase to perfect planning.
Phased Roll-Out: This will be a phased introduction department by department. Though a phased implementation will allow the system to be introduced with less disruption, coordination of data both in the old and new systems until full implementation will be necessary.
3.2 Reduce Patient Volume Temporarily
In the go-live period, it is recommended to decrease the number of patients during the first week so that the staff could get used to the new system without extra pressure. This would prevent backlogs, reduce stress, and give staff a chance to learn and troubleshoot.
Modify Schedules: The schedules of appointments should be adjusted in a way to minimize the number of patient visits within the go-live week.
Schedule some buffer times between appointments so that the staff can get accustomed to the new system and any issues that crop up without compromising patient care.
3. 3 On-site Support
On-site support during the go-live phase is important in solving problems promptly. Dedicated teams are usually provided by EMR vendors to help staff during the go-live process, answer questions, and address issues as they arise.
Establish an On-Site Help Desk: Create a temporary help desk or small support team onsite to support on-the-spot support while the go-live is in effect.
Use Super Users: The super users who had been trained up to this point should help spread the word and lead others into using the system. Super users can be front line support, as well as real-time advisers for the staff.
3. 4 Monitor System Performance and User Feedback
Critical traces of technical and usability problems come in the first few weeks when online operation happens. Monitoring how the system has performed, besides user feedback, is essential for tracing problems as early as possible and arresting the scale to much more serious points.
Monitor Key Performance Metrics: This includes validation of EMR system performance against meeting, and probably even surpassing expectations. It can be systems’ response time, data accuracy, and even rates of error with user operations.
Collect Staff Feedback: Make the staff active in reporting what they see or experience. Feedback of this sort is invaluable when trying to point out areas which need more learning, help by the organization, or even by amending the system.
3. 5. Implement a post-implementation phase with support for continued maintenance
An EMR system requires constant maintenance and support in order to continue running and being applicable as the dynamics of the hospital change with time. Beyond the go live, a successful permanent support structures ensure the delivery of assistance to staff and sustaining the functionality of the system.
Set up a Dedicated Support Line: Using either an internal IT or vendor support, ensure that staff know how to access help when needed.
Schedule Regular System Updates and Maintenance: The EMR systems are required to be updated periodically to ensure the system remains secure and effective. A schedule should be planned for periodic shutdowns to detect and correct problems that may affect system performance.
Ensure that the employees are continuously trained on the advanced capabilities and, at the same time, improve their skills as they gain more knowledge about the EMR system. This continuous learning might eventually lead to higher efficiency and better user satisfaction regarding the system.
3. 6 Evaluate the Implementation Process
Following the settling of the system post-go-live, there should be a time for reviewing the end-to-end implementation process. Successes and areas for improvement in the system are crucial feedback for any future alteration to the system or technology used.
Post-Implementation Review: Collect feedback from each department on how the implementation affected their workflows and where improvements could be made.
Document Lessons Learned: This is a summary of the major findings and successes as well as areas that need special attention. This white paper will be very useful in future projects.
The go-live stage is more than the implementation day; it is actually the transition period that will determine the outline of the level of the hospital–its connection with the EMR system. With direct connectivity, knowing performance, and designing for continuous improvement, hospitals have all there is to ensure a smooth and successful integration beneficial to staff and patients alike.
Why Healthray?
Healthray.com provides targeted resources and support for hospitals looking for a trusted partner in the implementation of best practices on EMR. They offer total solutions, targeted at enhancing workflow efficiencies, supporting data transfer, and meeting training requirements that ensure easy use of EMR. Healthray.com has a team of experts to support the hospitals in every step of the process, from planning through go-live support all the way and maintenance and optimization of services afterwards.
Healthray differentiates itself from a partner that can not only be there while the hospitals first sign on, but also keep the EMR system in good shape and compliant with industry standards. Working through Healthray.com hospitals can confidently manage the EMR transition, improve operational efficiency, and close the loop to better patient care.
Conclusion
The introduction of EMR software in a hospital environment is a challenging, but ultimately fulfilling, task. It changes how patient records are handled, how workflow efficiency is improved, and how patients can do better. But, successful rollout depends on systematic planning, team involvement, and high priority on compliance, and security.
Each step—from assessing readiness and setting goals to selecting the right vendor, training staff, and securing data—builds a foundation for a smooth transition. Post-implementation’s support and iterative optimisation guarantee that the Hospital Management System continues to be sensitive to the changing needs of the hospital and that effective use of the system over time is fostered through continuous training of staff.
Through the adoption of new technologies (e.g., AI, interoperability, cloud-based solutions), hospitals can get the best out of their EMRs in the long-term by maintaining their adherence to good clinical practice and technological progress of the industry.