Electronic health records are transforming the manner in which hospitals offer patient care. These digital systems replace bundles of paper-based health records and, instead, give health professionals an immediate point of access to critical data on any patient.
What does the whole EHR thing mean for the hospital administrators, IT teams, doctors, and nurses? Apart from convenience, EHRs create better coordination, efficiency, and accuracy in the process of care provision. There are also challenges like data security and system interoperability.
This post discusses the role of the EHRs in changing hospitals; their benefits, common hurdles, and actionable steps toward seamless implementation.
What are Electronic Health Records (EHRs)?

Electronic Health Records (EHRs) are digital systems that store comprehensive information about a patient. Unlike the traditional paper charts, EHR Software gives real-time access to a patient’s medical record, treatment plans, lab results, and more – all stored on a secure platform. In addition, the care providers and staff members interfacing with the patient are authorized to access information across departments or facilities to maintain effective communication, continuity of care, and the possibility of including other healthcare professionals when needed.
They usually involve:
- History of diseases: Diagnoses, past treatments, and allergies.
- Results of the tests: Quick references to laboratory and imaging reports.
- Medication records: This includes prescriptions that are currently being administered or are even also provided along with possible interactions.
- Clinical notes: Observations and updates made available from doctors and nurses.
In a hospital facility, for example, EHRs would go well beyond the basic functions of storing data. It would assist in decision making by providing a full picture of the patient status. For instance, in an emergency case, an EHR could provide the patient’s allergy history or recent lab results, thus saving lives.
Besides, EHRs work as a foundation for broader hospital operations e.g. streamlining the billing system, which allows data-driven decision making through analytics. These systems are not just tools; they are in fact a backbone of modern healthcare management.
Benefits of Hospitals EHR
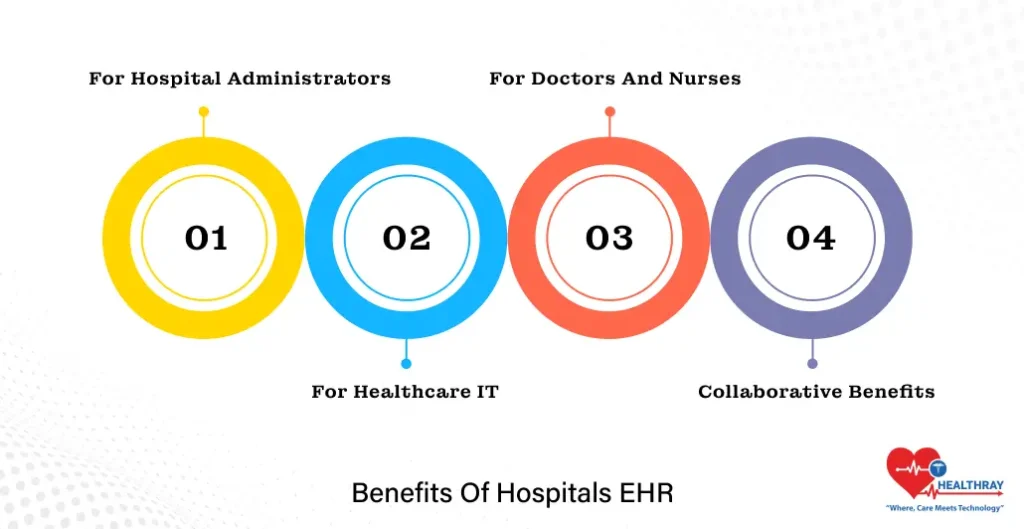
Electronic Health Records (EHRs) contribute to a wide array of benefits for hospital settings directly affecting the lives of administrators, healthcare IT teams, and medical personnel. Here is how the difference comes about:
For Hospital Administrators
1. Streamlining Operations: EHRs provide automation of repetitive tasks such as record keeping and billing. Reduction in administrative expense and resources (acquired through saving cost) can be freed for more strategic initiatives.
2. Cost Savings: Paperless records are good for storage cost reduction. Minimization in the number of billing errors or errors in patient documentation must also result in large savings due to the much fewer amounts to be paid for rectifications and reimbursements.
3. Data Insights for Decision-Maker: Use aggregated data provided by EHR systems to find trends, monitor hospital performance, and plan improvements in patient care and resource allocation.
For Healthcare IT
1. Better System Integration: Those EHR systems are built to work across other departments; thus, easy for IT teams to make the connection of other systems like the laboratory software, imaging platforms, and patient portals to work with added efficiency,
2. Advanced Security Features: Modern EHR systems include encryption and multi-factor authentication, hence helping IT teams in safeguarding sensitive data on patients.
3. Scalability: Cloud-based EHR solutions will be developed along with the hospital, hence making it manageable for IT personnel when it comes to expansion or system upgrades without overhauling the entire infrastructure.
For Doctors and Nurses
1. Improved patient care: Clinicians can make more informed decisions because of real-time access to entire informative patient medical records. For example, before prescribing a drug, knowledge of drug allergy prevents unnecessary adverse reactions.
2. Less error: Automated alerts in EHRs may sound the alarm for health providers on possible drug interactions, missed tests, or abnormal lab results.
3. Time saved: EHRs eliminate the time dragged searching for physical records or trying to speak to other departments. That frees clinicians’ times to think more about patient care.
Collaborative Benefits
These EHRs are also good tools for joining members. Everyone, from the top-level administrator to the bedside nurse, has access to the same updated information, creating better collaboration and less room for error.
With improved efficiency in enhancing care quality, EHRs pave the way for better outcomes from hospitals for patients or staff.
Implementation Challenges of EHR: An Overview
Despite the numerous benefits of Electronic Health Records (EHR), the implementation of it in the hospital has its own challenges. Most common challenges that hospital administrators, CIOs, and medical personnel face include:
Concerns about Privacy and Security
Shifting toward the digital system entails a very critical responsibility toward sensitive patient data and how to protect it. The threats are ceaselessly present, which are cyberattacks, data breach, and unauthorized access.
Key issues:
- Healthcare data is value-added in black markets for hackers.
- Unintentional employee errors will expose the data.
Solutions:
- Implementing stronger encryption protocols.
- Use multi-factor authentication to restrict access.
- Constantly conduct security audits and train staff on how to secure attention data.
Interoperability Issues
Most hospitals are unable to bring their EHRs into integration with other systems or across healthcare networks, resulting in a rupture in information sharing that hinders collaborative care.
Key Issues:
- The EHR from one vendor can’t communicate with others from different vendors.
- Disparity in sector regulation towards data sharing.
Solutions:
- Select EHRs that comply with interoperability standards such as FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources).
- Use APIs to enable easier and better integration of existing software at hospitals.
User Adaptation
The introduction of EHR systems usually alters established work patterns-and thus resistance from staff. New systems may seem unintuitive, slow, and may compromise efficiency for doctors and nurses.
Key Issues:
- Steep learning curve of the in-house untechnologically-savvy staff.
- Frustrations due to the symptoms presented by system bugs or slow-or-non-responsiveness.
Solutions:
- Comprehensive training for all targeted roles.
- Ongoing support for issue-resolution and feedback collection.
- Include end-users in the process for their choice of friendly platform.
Requirement of High Upfront Investments
Implementation cost of EHR systems can be high, especially for smaller hospitals. Costs associated with EHR systems are: software licenses, hardware, staff training, and recurrent maintenance.
Key Issues:
- Difficulty in acquiring funding for large transitions.
- Delayed return on investment.
Solutions:
- Govt. incentives or subsidies for EHR adoption should be considered.
- Gradual implementation should be done instead of a single modular entry.
Workflow Interruptions
Sometimes, hospitals experience workflow interruptions during implementation. This can cause slow patient processing times or patient processing errors when staff is unfamiliar with the system.
Key Issues:
- Initial inefficiencies during the transition phase.
- Loss of patient satisfaction.
Solutions:
- Test the EHR system in selected departments before rolling it out completely.
- Provide extra support staff during the transition.
The resolution of these challenges requires proper planning, collaboration, and a long-term commitment for optimization. These hurdles can be overcome by hospitals, and it realized the full potential of EHRs to ensure smooth operations in good efficiency.
Best Practices for Successful EHR Implementation

For their successful implementation, EHRs need to be already planned, with an exchange of communication, being prepared for technology as well as the people. Here’s a sneak peek into how your hospital can get the best out of EHRs with the least inconvenience:
Define Clear Goals
Begin by asking what an EHR system should achieve. Be certain that the objectives relate to the hospital’s interests: improving patient care, lessening administrative burden, and data protection, for example.
Steps:
- Chart the goals, i.e., a 20% decrease in charting time; greater accuracy in medication tracking.
- Communicate these goals to all stakeholders, so everyone is aligned on the purpose of the implementation.
Select the Right EHR System
Choosing the right electronic health record (EHR) system is paramount. It has to meet the needs of not only administrators, clinicians, and IT teams but also regulatory requirements.
What to Look For:
- Intuitive interfaces that facilitate adoption by medical staff.
- Compatibility with the hospital’s existing systems.
- Features such as automation, interoperability, or mobile access.
Tip: Include end-users (e.g., doctors, nurses, IT staff) in the selection process so that their needs are taken into account.
Invest in Comprehensive Training
Training ensures that staff can use the EHR system efficiently. In the absence of training, even the most sophisticated systems will fail.
Best Practices:
- Training should be role-specific: administrators, IT professionals, and medical staff have different needs.
- Use role-play, simulations, and hands-on approaches.
- Ongoing support, like help desks or refresher training, is offered to help personnel champ at questions that come up.
Pilot the System
Rather than hastily adopting the EHR across your entire hospital, assess it first on a smaller level; that is, pilot it. Pilot programs help in working through problems and gather feedback for refinement.
Ways to Pilot Effectively:
- Testing should be conducted in a chosen department or unit.
- Monitor for workflow and collect feedback from users.
- Use insights from the pilot phase to modify changes before going ahead with full-blown operations.
Data Security and Compliance
Patient data security is paramount. If a system is protected, confidence is established toward it, and their legal compliance is assured.
More Pointed Actions:
- Bring into practice strict cybersecurity safeguards, including encryption and regular audits.
- Train your staff to handle data in accordance with avoiding accidental breaches.
- Be in the know about the developments in the healthcare regulations and make adjustments in your systems.
Workflow Integration
The EHR should enhance workflow, not disrupt it. Preparation for implementation must run parallel with its integration into daily operations.
What to Do:
- Instead of forcing staff to adapt to a generic setup, customize the system to fit within the hospital’s workflows.
- Automation needs to be used to eliminate manual tasks like data entry or appointment scheduling.
- Collect feedback regularly for assessment of places where the system could integrate better.
Track Progress-Continuously Improve
EHR implementation is never complete after deployment. Besides continuous evaluation, updates will offer the best opportunity for systems optimization.
What Keeps the Momentum:
- Success can be measured against performance metrics such as reduced charting time or fewer clinical errors owing to documentation.
- Refinements can be made to the system on the basis of user feedback, allowing facial recognition features to evolve for better accuracy.
- Regularly updating software is regarded as a necessity for feature requests or emerging needs.
As a result of these best practices, hospitals can ensure good preparation for a smooth and effective EHR implementation. This will thus lay the groundwork for better patient care delivery, operational efficiency, and the working environment of staff.
Conclusion
Electronic Health Records (EHRs) transform the hospitals by redefining how patient data is managed and utilized. From ensuring the wellbeing of patients to improving the administration of processes, EHRs are now an important part of modern health practice. However, implementing EHRs raises challenges with data security, interoperability, and user adaptation that need to be carefully factored in and are never far from the organization’s mind.
As hospitals look to the future, EHRs will become stronger than ever with advances in AI, data analytics, and interoperability. Not only will EHRs store patient data, but they will enable smart clinical decision-making and drive personalized care. For hospital administrators, IT professionals, and clinical staff, success will call for investing in the right Hospital Management System and building a culture of collaboration and learning. By heeding the good that comes with EHRs and putting out fire on the challenges, hospitals can have the entire suite of EHRs functioning with full might to provide better outcomes and satisfaction for both patients and staff.