AI also brings in much efficiency and insight into patient care in the management of electronic health records by the hospitals themselves. Automating routine tasks, offering analytics in real-time, and improving decision-making-the AI-driven EHRs make life much easier for healthcare providers while at the same time improving patient outcomes.
In this article, we explain how AI is integrated into EHR software, real tangible benefits that are delivered from it, challenges that come up, examples from the real world, and emerging trends shaping the future of AI in healthcare.
Benefits of Integrating AI into EHR Systems
AI is making EHRs dynamic-from being a static repository of information to being active in the continuous improvement of both hospital operations and patient care. AI Impact of AI-EHR in patient outcomes shows measurable benefits by enabling earlier risk detection, reducing documentation errors, and supporting more accurate, data-driven treatment decisions. Here’s how:
Smoothening Administrative Burden
The majority of the time in hospitals is consumed by their staff for documentation, data entry, and management of charts. AI-powered tools automate these processes, reducing administrative burdens. For example, NLP can transcribe clinical notes in real time, hence allowing physicians to focus more on patient interaction rather than paperwork.
Improving Clinical Decision Support
AI will be further integrated into EHR systems to enable analytics on patient data for actionable insights. Predictive analytics can be deployed as an early warning system to alert providers to potential complications, often well before they occur, such as early signs of sepsis or adverse drug interactions. These are rapidly becoming additional layers of support to enhance decision-making and reduce the risk of human error.
Improving Patient Outcomes
By integrating the element of AI, a hospital will be able to identify those patients who are at a higher risk and develop special individual care plans by using both historical data and real-time metrics to come up with better treatment effectiveness and better recovery rates. These are insights that can enable AI-driven reductions in hospital readmission rates by proactively addressing the health needs of the patients post-discharge.
Smoothening Work Processes
AI algorithms further enable smarter prioritization, hence optimizing scheduling for better resource utilization. By doing so, machine learning models are able to predict what times of day or month will most likely see high admission rates, aiding the development of effective staffing and resource allocation strategies in hospitals. This reduces wait times and improves patient flow.
Bolstering Data Accuracy
Poor data quality in EHR could have serious consequences on patient care. AI-driven tools review and make corrections to entries in real time, further ensuring integrity of the record. Better accuracy will instill more confidence among health professionals in the use of the data within the EHR.
Supporting Population Health Management
AI analyzes large volumes of data to find patterns and trends in patient populations that can yield insights useful for addressing the challenges confronting the broader public health. This may range from accelerating the time to outbreak identification to improving care for chronic conditions. This capability enables proactive measures and a much more strategic approach toward healthcare delivery.
Implementation Strategies for AI in EHR Systems
Deployment of AI in EHRs needs serious thinking, planning, and execution to make it successful. Hospitals must address technical, operational, and human issues in a manner that best optimizes the potential of AI. Some important strategies to consider include:
Assess exiting infrastructure
Equally important is the assessment of the EHR and IT infrastructure of the hospital prior to the implementation of AI. This is because there is always an issue of compatibility, and AI solutions must be integrated into the existing platforms. This will also bring into focus some of the gaps that need attention, like outdated software or inadequate storage of data.
Involve Multidisciplinary Teams
The process of integration requires collaboration among hospital administrators, IT professionals, clinicians, and AI vendors. All bring their unique perspectives to ensure solutions are not only technically and clinically suitable but also easy to use.
Prioritize Data Quality
AI algorithms require quality and organized data. This includes cleaning and standardization to avoid errors and biases. In this vein, quite importantly, regular audits with the use of tools that validate the integrity of the data become of utmost importance.
Investment in Personnel Training
Any introduction of AI in EHR systems will be successful only if the staff are confident using the new tools. Training programs should be practically oriented rather than technically focused on AI-powered features. Hands-on workshops and ongoing support can ease the transition.
Address Security and Compliance
Cybersecurity should be the main priority since AI works in EHR systems, handling sensitive patient information. The outline of encryption protocols should be done appropriately in hospitals and adhere to HIPAA regulations. Regular security audits will help with the threat of potential breaches.
Begin with Small-Scale Pilot Programs
Rather than deploy the AI throughout the hospital, it makes more sense to have a pilot program in one department, such as radiology or patient scheduling. Pilot programs are very beneficial to test, gather feedback, and fine-tune the system before wider implementation.
Scalability – The Focus
This means that as hospitals grow, along with the needs and requirements of patients, so must AI solutions. Ensuring flexibility within systems and that they will meet future demands provides a long-term return on investment.
Monitoring and Evaluation
These hospitals should continue to monitor the impact of AI on operational efficiency and patient outcomes after implementation. Periodic reviews against benchmarked outcomes, based on
Challenges and Considerations in AI Integration for EHR Systems
Although AI offers immense transformative potential in EHR systems, this technology also entails its own challenges, which must be considered at the administrative level in hospitals. Being able to recognize and prepare for these obstacles makes integration much smoother and maximizes benefits. Some of the important considerations are:
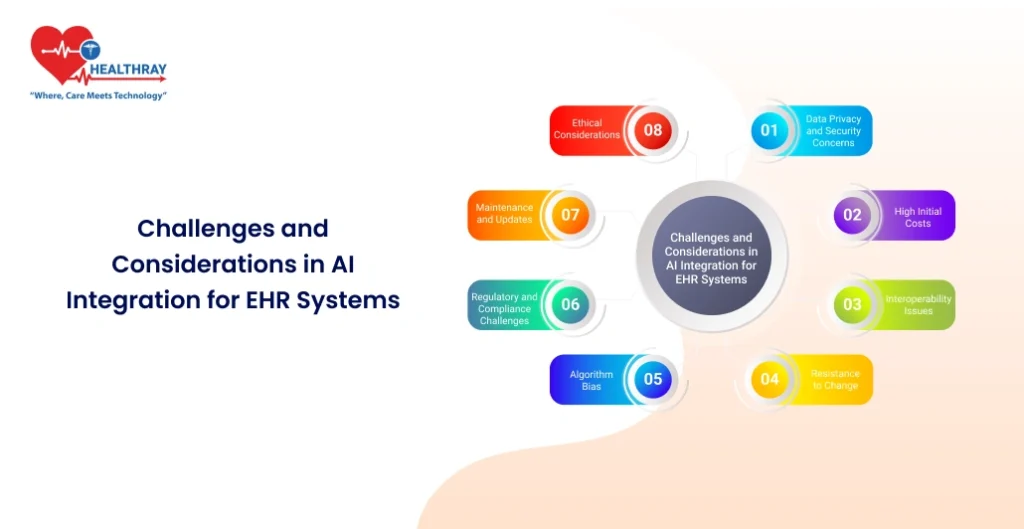
Data Privacy and Security Concerns
EHRs contain very sensitive information pertaining to patients. Adding A.I. increases the risk associated with data breaches and unauthorized access. Due to this, multi-factor authentication, encryption, and periodic assessments about system vulnerabilities require huge investments in cybersecurity by hospitals.
High initial costs
The big disadvantage with AI is the huge upfront investment required in the form of software, hardware, and training. From a financial perspective, the smaller hospitals may not be in a position to invest in these systems. A careful cost-benefit analysis and a step-by-step implementation can overcome financial challenges.
Interoperability Issues
Most EHR systems are on different platforms, and it is tough to integrate AI into them seamlessly. There is a possibility of a lack of standardization across systems, resulting in less effectiveness due to data silos. This requires collaboration on the part of the vendors with regard to compatibility and use of open standards.
Resistance to Change
Possible resistance factors that could keep staff from embracing AI include the fear of being replaced by it and unfamiliarity with the technology. Open communication to dispel myths about AI and strong training programs therefore play an important role.
Algorithmic Bias
AI models run the risk of propagating bias in existing health data. For instance, patient populations that are under-represented may not get as accurate predictions or the best recommendations for their care. Ongoing auditing and diverse data inputs hold the key to reducing bias.
Regulatory and Compliance Challenges
Medical AI must completely comply with regulations such as those provided by HIPAA in the United States or the General Data Protection Regulation in Europe. Navigating these frameworks is tricky, laborious work and usually holds up implementation. Hospitals need to cooperate with legal experts who ensure that compliance is attained without giving away functionality.
Maintenance and Updates
Such systems should have continuous updates for effectiveness and security through frequent recalibrations of algorithms, patching of vulnerabilities, and adaptation to continuous changes in healthcare protocols. In other words, resources should be available for long-term maintenance.
Ethical Considerations
Relying on AI for critical healthcare decisions raises ethical questions. Transparency in how AI algorithms work, coupled with accountability for errors, needs to be established to create trust among both the patients and clinicians.
Future Trends in AI and EHR Systems
The advancing AI technology further promises greater changes in the functionality of Electronic Health Record systems. A look at the emerging trends that will shape the future of AI in healthcare:
Wearable Device Integration
Next-generation, AI-enabled EHR systems will increasingly incorporate data from wearable health devices, including activity trackers and smartwatches. Data such as this-in real time-gives the clinician a more comprehensive picture of a patient’s health with which to inform proactive care and personalized treatment plans.
AI-driven predictive healthcare
The EHR systems will use advanced AI algorithms in the future to better predict patient outcomes. For example, AI will pinpoint potential health issues like heart attacks or diabetes several years in advance by considering past data and lifestyle patterns.
Voice-Activated EHRs
Voice-enabled AI assistants will be common in EHR systems. Such assistants will allow clinicians to update records, retrieve patient information, and receive alerts without their having to type a word, further speeding up data entry and making it more intuitive.
Improved Interoperability
AI will play a key role in breaking down the silos among different systems in healthcare. The use of AI allows for fluid data exchange and standardization, thereby assuring accessibility to patient records and their uniform availability across organizations for better care coordination.
Patient-Centric AI Tools
In the future, more AI-powered tools will be directly aimed at patient empowerment. For instance, AI chatbots embedded in EHR portals are going to let patients understand their medical records, manage their appointments, and get personalized health advice-further boosting patient engagement.
Genomic Data Integration
With the evolution of genomics, genetic information integrated into patient records will also form a part of AI-driven EHR systems, thus enabling more correct diagnosis and treatment, with greater personalization-for example, of therapies in oncology or the treatment of rare diseases.
Automated Risk Management
Improvement in risk management with the use of AI will be achieved through constant monitoring of various EHR data anomalies, showing compliance issues, billing fraud, or data breaches. These systems will provide real-time alerts to enable hospitals to act with speed in mitigating risks.
Augmented Reality in EHR Visualization
AR, combined with AI, will revolutionize the way clinicians view EHR data. For example, AR tools could project 3D information about a patient related to a surgical procedure or display interactive graphics that facilitate discussion about complex cases.
AI and Blockchain for Secure EHRs
The convergence of AI with blockchain technology is likely to greatly reshape EHR security. While blockchain ensures data integrity and transparency, AI analyzes blockchain for possible security threats. In that way, it will set up a very robust mechanism of defense against cyberattacks.
Continuous Learning Systems
Future AI in EHRs will make use of machine learning models that get updated automatically with the addition of new data. The self-improving systems will mean recommendations and analytics that continuously become more accurate and relevant over time.
Conclusion
AI is changing the face of EHR systems. For hospitals, it is proving to be a strong tool in ensuring more efficiency, better decision-making, and improved patient outcomes. From automating administrative tasks to predictive health care and personalized treatment plans, AI applications range across the board. However, there are challenges in the form of high implementation costs to AI adoption, privacy concerns, and training for staff. Thoughtful strategies towards these barriers ensure successful integration and long-term benefits. Real-world examples, such as those from Mayo Clinic and Geisinger Health System, have shown AI’s transformative potential when well applied. In the future, AI’s role in Hospital Management Systems will only expand, with trends such as wearable device integration, patient-centric tools, and genomic data analysis. It would mean a gradual introduction of more efficient ways of dealing with demands that seem to keep growing in the healthcare sector. As AI continues to improve incrementally, its integration with EHR systems will be at the forefront of moving toward a more efficient, patient-centered healthcare ecosystem.




