Introduction
The deployment of EHRs into the hospitals transforms the way hospitals document the information of patients. Like paper records, the latter stores the information in an electronic format and, upon authorization, allows the right healthcare provider to have a view of it instantly. Cutting the stack of paperwork, it will even improve the decision-making for healthcare professionals and smooth workflow. EHR Software thus enable effortless.
Main Characteristics of EHR Systems
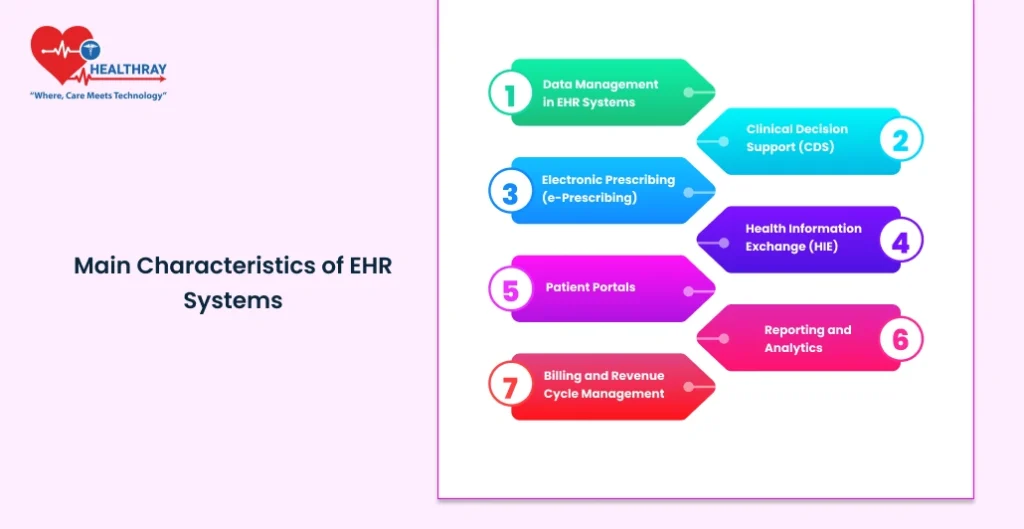
EHRs provide many functions for proper fluidity in patient flow and services. Core competencies, however will be the essence to help the health care manager as well as the technologist gain an eye-opening view concerning efficient implementation of EHR. Now, see some of the best features with which hospitals may find it productive to use.
Data Management in EHR Systems
All information regarding the patients, such as demographic information, medical history, diagnosis, treatment plan, immunization records, and lab results, are put centrally. Thus, health care providers get a wide view of the patient by looking into the complete profiles and make more informed and timely decisions.
Clinical Decision Support (CDS)
An enhanced clinical decision support system helps the physician and the other providers review the patient’s data to bring up alerts, reminders, or recommendations. It can identify for a provider such drug-to-drug or drug-disease contraindications, remind of due preventive care, or point out an alternate treatment based on a patient’s history, to name a few. It provides safer, more evidence-based care.
Electronic Prescribing (e-Prescribing)
Electronic prescription enables a prescriber to send prescriptions electronically to pharmacies and eradicate mistakes attributed to handwriting, and also reduces clerical work. EHRs make prescription processes easier, which enables access to all medication histories and allergies of a patient, thus minimizing the chances of adverse reactions to drugs.
Health Information Exchange (HIE)
This features share the data of the hospitals, clinics, labs, and other health care providers. This sharing is invaluable when one changes from one care setting to another ensuring the medical history transported with him and the continuity of care.
Patient Portals
Most EHRs offer a patient portal that a patient can gain access to their electronic medical record, request an appointment with the providers, or even communicate with them straight away. This activates the patient in acting more upon self-care practices as they are more connected and satisfied with care.
Reporting and Analytics
Reporting on such metrics as patient outcome and readmission rates and productivity tracking of personnel at hospitals are powerful analytics from EHR systems that make hospitals analyze what their metrics are hence creating and offering an improved quality of service delivery. All this is according to regulations regarding the provision of health services.
Billing and Revenue Cycle Management
They deal with the managing of insurance claims, billing, and payments which integrate the whole billing process for the EHRs. Minimize the administration workload and decrease the error costs involved in billing. It will be transparent enough for the patient to understand and comprehend their own billing. And every one provides an extra mileage as to the efficient way for how care can be made along with the improvement of the overall processes.
With many options available, it becomes significant for the hospitals to make a proper selection of feature that will work efficiently along with the requirement of the hospitals, workflows, and budget.
Types of EHR Systems: On-Premise, Cloud-Based, Hybrid
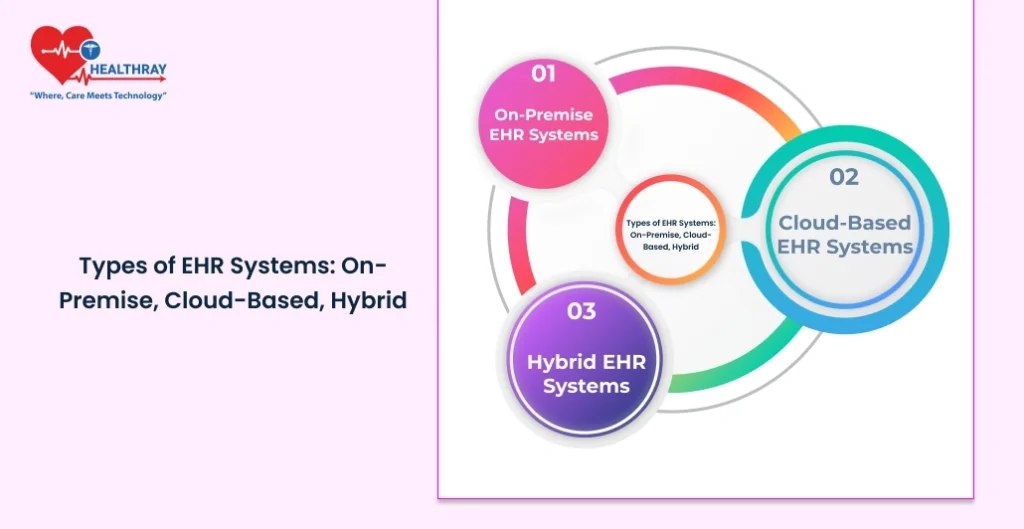
When it comes to EHR systems, there is a choice. All of them vary in regards to pros and cons. It depends on which one to use, according to budget, IT support level, and data security level preferred. Here is an overview of the main types of EHR systems that exist currently in hospitals:
On-Premise EHR Systems
Overview: On-premise EHRs are directly installed and stored on the facility owned servers at the hospitals. All rights like storage and security of the system will be hospital owned.
Advantages: On-premise EHRs have much better control over data privacy and security because they handle highly sensitive information about patients.
They rely much less on the stability of the internet, a very critical point in some areas where internet stability is un-reliable. Some of the problems involve on-premise systems’ installation cost, including their hardware and software, and additionally, the costs of IT support. Further from that, an area and source must be exclusively provided to provide for the area where the server and data storing are located and be kept secured and accessible at all times.
Cloud-Based EHR Systems
Overview: EHRs will be kept offsite in third-party-hosted servers. Systems will be accessed over the internet so that hospitals can avail themselves of higher-level functionalities of EHRs, which do not require a heavy upfront investment in infrastructure on the site of a hospital.
Advantages: Relatively easier in the initial stages since most prefer the subscription model and the solutions scale well, thereby allowing a hospital to change easily with increasing needs. Data redundancy capabilities are high and by the system such that the same data does not get lost like cases from local servers.
Challenges: Though cloud-based EHRs are less cumbersome, their dependency on the availability of Internet connectivity is one challenge. Furthermore, any interruption in connectivity can easily make the applications come to a halt. Another shared responsibility related to security is that the hospitals too need to depend on EHR providers having maximum possible data security control for keeping patient information confidential.
Hybrid EHR Systems
Overview: The two systems encompass cloud-based as well as on-site elements hence coming in to bring a compromise situation for those healthcare institutions seeking convenience. Most health care hospitals usually store vital sensitive information at onsite while uploading insignificant data through clouds or vice-versa.
This approach gives hospitals more control over sensitive information while still enjoying some of the cost benefits and scalability of cloud-based solutions. Hybrid EHRs allow hospitals to adapt their data management approach based on specific needs.
Challenges: Hybrid management is going to be challenging as on-site data synchronization into the cloud environment would be required to take place. It entails the hybrid system possessing very high strict security arrangements concerning protecting data storage on the other media storage thus adding more complications to IT as well as expense. Choosing the Right Kind of EHR
The decision regarding on-premise, cloud-based, or hybrids will be unique to a hospital and the priorities driving those choices. Larger hospitals with stronger, dedicated IT teams may opt for on-premise solutions, whereas smaller facilities may find cloud-based more accessible. Hybrid systems appeal to hospitals seeking flexibility and control, yet these systems require more robust technical support.
Implementation Challenges and Solutions
One of the key implementations, developed recently, is an EHR system, which has many logistically, economically, and managerial issues that most probably influence its adoption. Therefore, managers and the IT group should also be aware and prepared for probable difficulties. Thus, here are some general hospital problems and their probable actions for solutions:
Too Costly Deployment
Challenge: EHRs are very expensive systems, including high up-front costs, as well as the purchase of software licenses, hardware, and other installation requirements. Most hospitals, especially the smaller ones, cannot afford these kinds of capital expenditures.
Solution: Rollouts can be phased within cost management. Hospitals should opt for a hybrid EHR or cloud-based subscription that allows spreading costs based on monthly and yearly commitments instead of requiring a tremendous sum at a time.
Staff Training and Adaptation
Challenge: It would introduce the administrative staff with a new system to which providers of health care would become habitual and perhaps not productive as well as poor-quality care providers, if they did not get adequate training.
Solution: Time for hands-on training, modules specific to a role, as well as ensuring that support in becoming proficient within the EHR is integrated together. Refresher courses and regular updates are fine ideas, ever accessible-say, system updates, for instance.
Migration of Data from Legacy Systems
Problem: Huge amounts of data pose a problem when migrating data from paper-based older records or old digital systems.
Therefore, the hospital focuses on critical data for smooth migration. A lot of planning takes place, from medical history about the patients and their treatment plans. Dedicated tools to migrate the data accompanied by consultancy from the IT professionals will ensure accuracy, hence not let the disruption influence it much. Periodic checks in the phase of migration, followed by one after migration would ensure that no breach of the integrity of data is made.
Interoperability with other systems
Problem: They also employ other electronic systems-from imaging to billing-that the EHR will need to interact with. Interoperability would result in workflow silos and partial data sharing.
Solution: Compatibility with those other systems will be achieved if the EHR uses open standards and APIs. It can adapt interoperability standards and those of ONC at the same time as it incorporates into installed software.
Data security and compliance
Challenge: EHRs contain sensitive information of patients; therefore, security of data becomes the first priority. Hospitals are also bound by HIPAA-like regulations that safeguard the data against breaches.
Solution : A holistic approach for data security includes encryption, two-factor authentication, and auditing data regularly. An emphasis on teaching staff best data security practices may ensure no access to the data is done outside of their assigned authority. Proper protocol in hospital data management processes should be communicated.
Smooth Working Process Upon Implementation
Probably, the daily work of the departments would be slowed down. The worst part is that care delivery will slow down.
Solution: The rollout can be done department by department to avoid disturbing the smooth operations of the service. In each department, super users or champions may be selected to master EHR, which then coach other members. More so, change can ask for staff input about their perceptions on what may need tweaking.
An EHR would be effectively implemented only with proper planning and the appropriate flexibilities and support systems at the right moments. With all these problems overwhelmed by such an approach in hospitals, the advantages of an EHR system would all be achieved if technology was applied effectively.
Data Security and EHR System’s Compliance
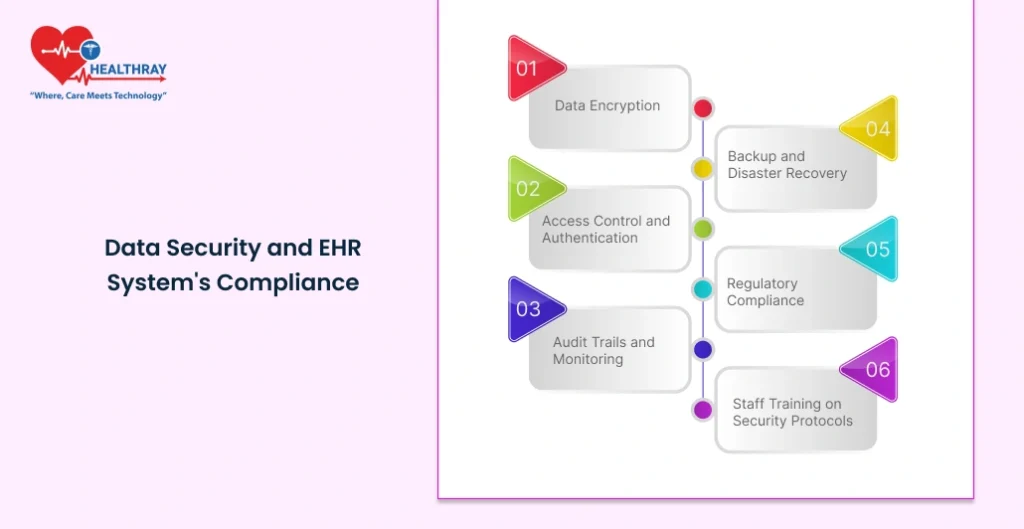
Data security and compliance to the regulations are major factors in running an EHR system in any hospital. These electronic health records contain sensitive patient information, which is confidential; therefore, these hospitals are accountable for maintaining such confidentiality. In most countries, legislation like Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act in the United States transcends legal liability; it is part of the process of winning patients’ hearts. This is a comprehensive review of some of the major compliance and security issues that hospitals must address when implementing EHRs.
Data Encryption
Overview : The very basics of security measures include data encryption, which will transform patient information to illegible codes. Authorized personnel with the decryption key will be those able to read the information.
Best Practices: At-rest and in-transit encryption ensures the protection of data stored on servers as well as the moment when data is transferred from one device to another. Moreover, updated encryption protocols offer protection against constantly emerging cyber threats.
Access Control and Authentication
Summary: Access control is necessary so that the access to EHR is granted to only genuine persons. Apart from this, multi-factor authentication methodology provides further security.
Best Practices: Role-based access control allows hospitals to restrict sensitive information based on the role of each user. MFA reduces the risk of unauthorized access because a stolen password becomes useless when the second factor has to be accepted, like getting a code in a user’s phone.
Audit Trails and Monitoring
Overview: All EHR-related activity should be caught by the audit trails. A record of any access report who accessed what, and when is also essential to be captured. The information in the records would trace the suspicious activities involved in accountability.
Best Practice: The hospital should have automated monitoring system for processing access log and alert mechanisms to alert network administrator of anomaly activity. Auditing of policies is done constantly, and an incident related to security is reported immediately.
Backup and Disaster Recovery
Overview: With hospital data backup, patients are quickly recovered should erasure or computer failure and data breaches, both accidental or a cyberattacks on the facilities cause the event to occur.
Best Practice: Hospital must have on-site and off-site data backups that will maintain redundancy. The hospital should regularly test its disaster recovery plan to ensure that backups work and that it can recover its data in case of an event in the shortest time possible.
Regulatory Compliance
Overview: Health care and EHR systems need to meet many regulatory requirements that indicate standards for privacy, security, and interoperability. For instance, the HIPAA act outlines principles on how to handle the data of the patient while ONC and CMS stipulate standards on meaningful use and data exchange.
Best Practices: Hospitals can ensure that their EHR system is compliant with the regulatory requirements through regular compliance audits. Documenting compliance efforts and training staff on regulations also help avoid potential legal and financial penalties.
Staff Training on Security Protocols
Besides that, security is not just about technology but also about action-taking by every individual who accesses the EHR. Staff training on security best practice reduces the risk of human error, which is often the most common cause of breach.
Best Practices: All the new entrants should go through security awareness and be revised annually. Other areas of this might include maintaining sensitive data or privacy, fighting phishing, etc.
Compliance and security keep the trust given by the patients intact; always ensure that hospital operations are entirely compliant with regulatory laws, which will also ward off expensive security breaches.
Conclusion
For instance, in hospitals, it has emerged quite highly indispensable regarding smooth workflow as well as due to a high level of care to the patient while meeting better needs for the data security as well as data compliance. Accessing any such information enlighten better and also timely decision-making for health workers with aggregation information into one electronic format. Although there are many planning processes, a huge investment and coordination for implementing an EHR system to be included in the hospital management system, it is not found to be aligned with the needs of the hospitals and does not get fulfilled as per the regulatory requirements.
Proper implantation of an EHR for the healthcare administrator, IT professional, or decision-maker would help bring the cost of operation down, quality in the care provided, and support later innovations such as AI and telehealth. Right type of EHR on-premise, cloud-based, or hybrid depends on data security compliance and ongoing training in the holistic structure of a Hospital Management System.
With superior technology, EHRs will be much more robust and powerful, with capabilities that would offer predictive insights, support interoperability, and enable patient engagement. Proper awareness of these trends and proactive implementation will enable hospitals to use EHRs not only as digital record-keeping but as transformative assets in the modern healthcare Hospital Management System.