Electronic Health Records (EHRs) have spearheaded a change in the inpatient delivery of care, by putting the relevant patient information into the clinicians’ reach. These digital architectures are the drivers transforming the hospitals and multispecialty medical centers rapidly improving the time to deliver the care and reducing the incidence of errors through prompt and precise access to patient information. Therefore, each member of the treatment team (that is, each one of the treating professionals) is able to take better, faster decisions, with a direct impact on quality of care and safety.
But EHRs go beyond simply storing patient data. They also cross departments, centralize administrative work and give patients more of a say in how they manage their care journey. In this article, we’ll look at how EHR software improves patient care, boost operational efficiency, and what challenges hospitals face when implementing them. Whether you’re just starting with EHRs or looking to make your current system work harder for your hospital, there’s plenty to explore.
Benefits of EHR Systems in Improving Patient Care
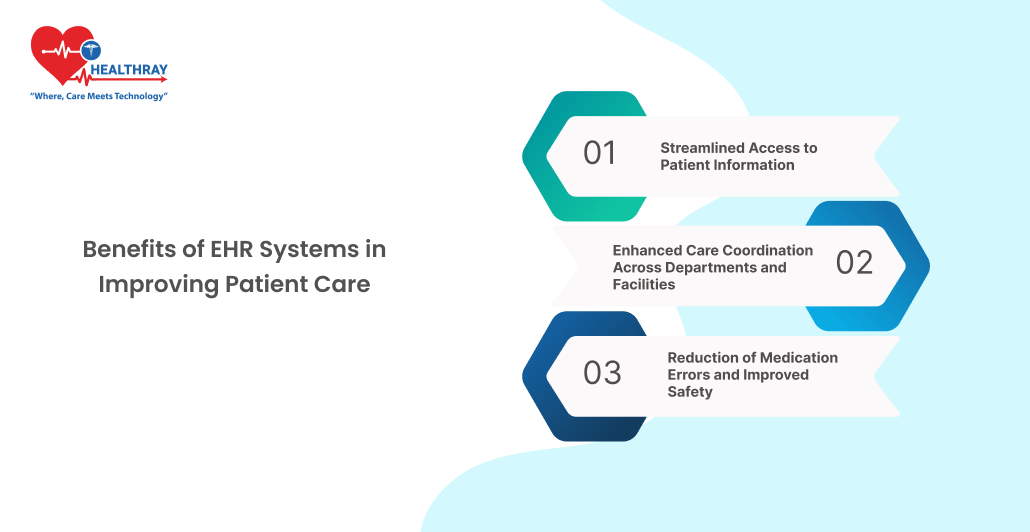
Streamlined Access to Patient Information
EHR systems provide immediate access to a patient’s entire medical history, current medications, allergies, and recent lab results. This rapid access offers the possibility to clinicians to make a precise, current decision, not waste time to find results. During crises such as emergencies, EHRs enable providers to rapidly retrieve a patient’s critical information, including allergies, thereby reducing potential risk from nondetailed patient histories. Specialists and general practitioners also benefit because EHRs update everything, and therefore make it easier to provide better coordination and better patient care.
Enhanced Care Coordination Across Departments and Facilities
For hospitals and multispecialty centers, care coordination is crucial when patients interact with multiple specialists or need complex treatment plans. The popular electronic health records software bridges communication gaps, connecting departments in real-time and ensuring that all providers have consistent, up-to-date information. This improved coordination prevents redundant tests, boosts treatment accuracy, and reduces care delays. As a result, patients experience higher-quality care, and hospitals save costs by streamlining their services.
Reduction of Medication Errors and Improved Safety
Safety features, including warnings about potential drug drug interactions, drug allergies and other contraindications, are implemented in EHRs. These alarms reduce rates of prescription errors, and better protect patients in this way. For example, if newly prescribed drugs do not conflict with a patients current medications, the system alerts the physician in such a way that a safer alternative can be selected. Research also indicates that medication errors are a major issue in healthcare and that EHRs are able to reduce these errors by maintaining accurate, current medication information on file for every patient.
EHRs for Patient Engagement and Self-Care
Patient Portals and Accessibility
EHR-enabled patient portals are transforming how patients engage with their own healthcare. Through these portals, patients can access their medical records, lab results, and treatment plans online, offering them a direct, transparent view of their health. Online access simplifies processes like appointment scheduling, prescription refills, and follow-up communications, saving patients time and giving them greater flexibility. With the popular electronic health records software, ease of access encourages patients to be proactive, keeping up with appointments, following care plans, and addressing health questions promptly.
Empowering Patients in Their Health Journey
EHR systems empower patients with more autonomy and knowledge about themselves by making that information available in their hands (i.e. This transparency allows, on the one hand, the patient to make an informed decision about the possibility of treatment, as a result of which adherence to drug regimes and to other forms of treatment can be increasingly promoted. EHRs- enable secure exchange of communication between patients and providers allowing patients to formulate questions, review instructions, or request clarifications even without having a scope with a physician face-to-face to see. Patient empowerment to actively participate in medical decision making is a potential way to rebuild the patient-provider relationship and resulted in a better long term health status.
Operational Efficiencies with EHRs in Hospitals
Reduced Administrative Burden
EHR systems minimize most common task in routine administrative work, thus, it significantly minimizes paper and manual data entry for hospital employees. By digitizing the patient record and automation of work processes, EHRs ultimately make this a cost savings opportunity for billing, coding and documentation for health care institutions and this is then translated to be an opportunity for hospitals staff in the freeing of administrative work. Scheduling tools integrated into Electronic Health Records also minimize appointment overlaps, send automatic reminders to patients, and reduce the number of missed appointments. These have the effect of increasing general productivity, i.e., personnel have more time to focus on patient care than on completing paperwork.
Cost Savings and ROI in the Long Term
Although the work of installing the EHR system occurs as an expenditure at the time of installation, hospitals often state that the EHR system produces significant cost reductions over time. Through the reduction of medical error, enhanced billing correctness, as well as less unnecessary testing, EHRs assist hospitals in reducing operation costs. Several HC organizations have demonstrated a positive return on investment (ROI) due to the EHR systems’ ability to increase levels of productivity, decrease staffing requirements for some activities, and increase receipts through more precise billing. The main cost-saving effect is not a direct reduction in cost but improvement in the efficiency of the hospital operation.
Data-Driven Insights for Population Health Management
Tracking Chronic Conditions and Outcomes
EHR systems are powerful tools for managing chronic diseases and monitoring health outcomes across large populations. With EHRs, healthcare providers can systematically track patients with conditions like diabetes, hypertension, or heart disease, enabling proactive interventions and personalized care plans. The popular electronic health records software helps healthcare teams identify at-risk groups and tailor preventive measures to improve overall health outcomes. Hospitals can also use EHR data to analyze trends and make informed decisions about resource allocation, care strategies, and public health initiatives.
Population-Level Health Monitoring
EHRs enable hospitals to track health measures at the population level, including rates of vaccination, prevalence of particular medical conditions, and other health reported measures. This level of tracking is of value for public health intervention and health care program efficacy. Hospitals and health care facilities can utilize this knowledge to optimize resource allocation, address community health requirements, and thereby improve public health outcomes. Data from EHRs also enable research and policymaking as they can consistently inform population health trend data.
Challenges and Considerations in Implementing EHR Systems
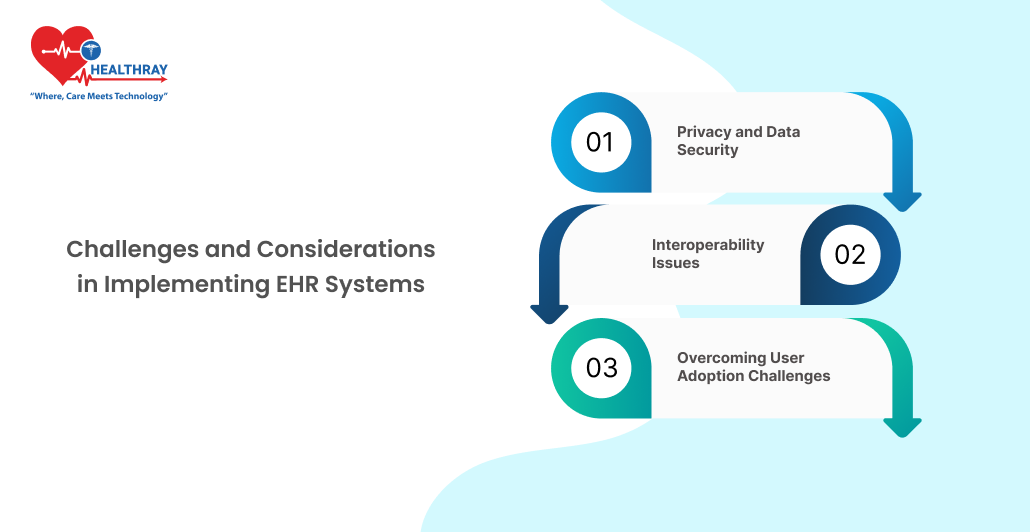
Privacy and Data Security
Given that patient confidentiality is of the utmost importance, EHR systems must comply with tight security requirements. In hospitals it is a matter of ensuring adherence to data protection regulations (e.g., HIPAA) that prescribe data encryption, access control and regular verifications to protect personal data. But it can also be a constant battle to keep up with security standards, especially in an era of increased cyberattacks. Hospitals must implement role-based access control and encryption in order to safeguard patient data while it is in storage or transit. Staff training is essential so as to avoid unauthenticated access and that all team members are familiar with the procedure for privacy.
Interoperability Issues
Interoperability, i.e., exchange of data among EHRs in other health care fields, continues to be a key challenge. Lack of standard data formats between different EHR systems can limit the system’s functionality, especially in multispecialty hospitals, who may need to export data to outside providers. Hospitals sometimes have to make additional investments in software or develop bespoke solutions in order to remedy incompatibilities between systems. Interoperability plays a key role in achieving coordinated care by facilitating smooth data exchange from which providers can obtain an overall health history picture of a patient.
Overcoming User Adoption Challenges
Healthcare workers may have to experience a steep curve when working with a new EHR system. Adaptation to digitalisation is costly and intrusive, resulting frustration in providers. Training and ongoing user support are crucial for the user to be able to adapt and hence reduce the disruptive one gets.
Some EHRs may not be customizable in a way that suits particular clinical practice, thereby adding to workflow issues. Offering direct training and allowing healthcare personnel to personalize EHR functions can increase adoption rates and, in turn, facilitate seamless incorporation of the system into the course of daily life.
Future of EHRs in Enhancing Patient Care

Predictive Insights with Artificial Intelligence (AI)
As AI is being increasingly integrated into healthcare technology, electronic health record (EHR) systems will be able to leverage the power of predictive analytics to help clinicians identify early health issues and intervene at an early stage of the problem. AI is able to examine big data sets stored in EHRs to estimate patient risk, for example predicting readmissions or future disease progression. These prognostic hints will allow clinical operators to take preventive actions and improve patient outcome through early prevention of disease. This approach could be, for example, highly viable to the therapy of chronic diseases, as well as for preventive care.
Enhanced Data Sharing Across Networks
There will be some new advances in EHRs in the direction of more sophisticated interoperability so that data can be smoothly exchanged across a health care network. Improved data sharing will enable interinstitutional teaming among providers at different facilities and systems to help care for patients by providing them with all required information when needed. In the future, due to the progress in data standardization of formats and the using of technologies, such as FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources), the clinical providers are going to face more smooth integration of healthcare data, which is critical to multispecialty patient management.
Personalized and Precision Medicine
As EHR systems continue to be developed, they will play an irreplaceable role in the realization of personalized medicine. Using data on patient genetics, lifestyle and exposures to environmental stressors next generation EHRs have the potential to guide providers to tailor therapies based on the unique needs of each patient. Precision medicine demands full information of the patient, and EHRs will be fundamental to their ability to store, analyze and extract these data that will allow generation of more personalized therapeutics. This methodology can lead to improved patient outcomes by matching treatments to patients’ individual characteristics and perhaps being able to minimize side effects as well as improve therapeutic response.
Remote Monitoring and Telehealth Integration
EHR systems will continue to expand their integration with telemedicine and remote patient monitoring technologies, as telemedicine takes its place in the future of healthcare. Use of this integration enables providers to monitor health data of patients captured by wearable and mobile devices as well as home environments directly from the EHR. This real time data access offers the chance to perform proactive health and pre-emptive care management and allow quick interventions, especially relevant for chronically ill patients, who must be constantly monitored.
Conclusion
Electronic Health Records (EHR) systems are revolutionizing the way that health care professionals and hospitals provide patient care. EHRs, providing benefits ranging from the optimization of record access to better organization and safety, offer various advantages that lead to improved patient outcomes and operational efficiency. In spite of setbacks in health system implementation (e.g., privacy problems, tradeoffs in interoperability and adoption) EHR systems are not replicable on the landscape of health care today.
As technology advances the potential benefits of a Hospital Management System continue to grow. Driven by artificial intelligence-informed, improved data sharing, enabling personalization of medicine and telemedicine, future EHR developments will allow hospitals to provide more precise and predictive medicine. For hospitals and multispecialty centers, optimizing their EHR systems can mean better health outcomes, improved patient satisfaction, and more efficient hospital operations.